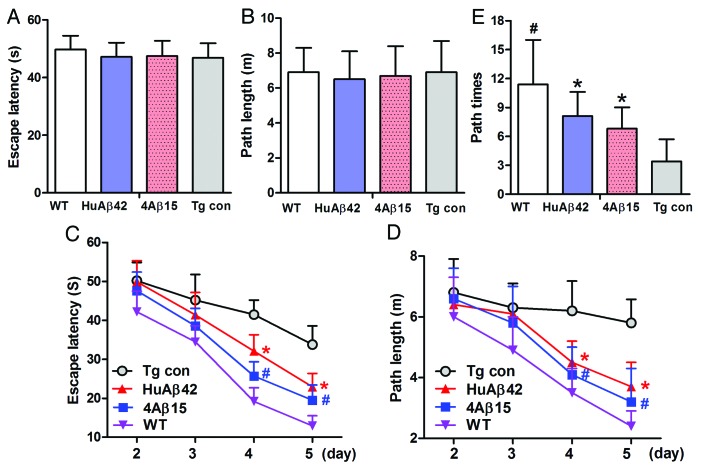
Figure 4. 4Aβ15 improves memory deficits in AD transgenic mice. A Morris water maze test consists of 1 d of visible platform tests and 4 d of hidden platform tests, plus a probe trial 24 h after the last hidden platform test. Animal movement was tracked and recorded. The 8.5-month APP/PS1 group mice and the same age wildtype group mice (WT) were tested. (A) During the first day of visible platform tests, both the 4Aβ1-15-treated, control APP/PS1 mice (Tg con) and WT mice exhibited a similar latency to escape onto the visible platform (n = 9, p > 0.05 by Student’s t-test). (B) Four group of treated and control mice had similar swimming distances before escaping onto the visible platform in the visible platform test (n = 9, p > 0.05 by Student’s t-test). (C) In hidden platform tests, mice were trained with 6 trials per day for 4 d. 4Aβ1-15-treated APP/PS1 mice showed a shorter latency to escape onto the hidden platform on the third and fourth day (n = 9, *#p < 0.01 by ANOVA). (D) The 4Aβ1-15-treated APP/PS1 mice had a shorter swimming length before escaping onto the hidden platform on the third and fourth day (n = 9, *#p < 0.01 by ANOVA). (E) In the probe trial on the sixth day, the 4Aβ15-treated mice traveled into the third quadrant, where the hidden platform was previously placed, significantly more times than controls (n = 9, *p < 0.01 by Student’s t-test).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.