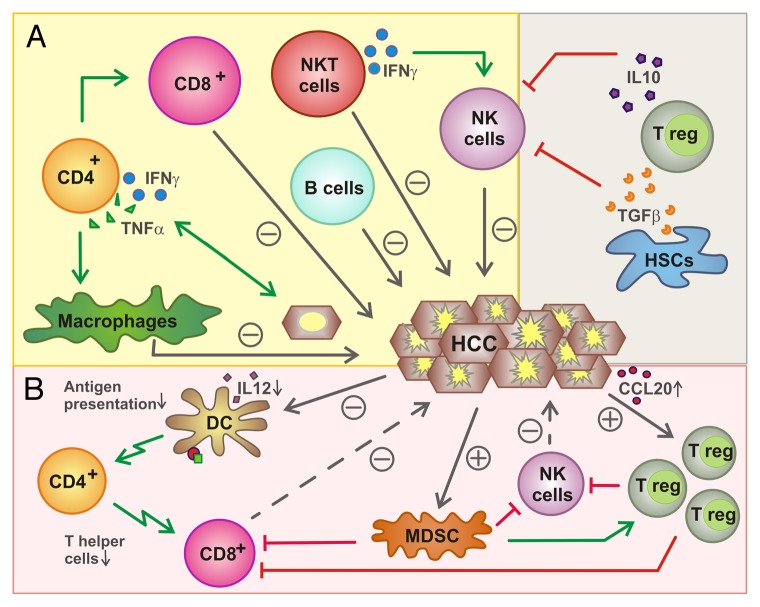
Figure 1. Functions of lymphocytes in liver cancer. (A) Influence of lymphocytes on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Several immune effector cells including natural killer (NK), NKT, B, CD8+ and CD4+ T cells have been shown to exert antitumor effects either directly (NK cells, CD8+ T cells, B cells, NKT cells) or upon the activation of other lymphocytes. Conversely, regulatory T cells (Tregs) mediate immunosuppressive effects, hence promoting oncogenesis and tumor progression, as they inhibit NK and CD8+ T cells. (B) Inhibition of lymphocytes by HCC. HCCs can recruit Tregs by a CCR6-dependent mechanism that impinges on the local secretion of CCL20. Tregs are also activated by myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and inhibit NK and CD8+ T cells. HCCs also limit the ability of dendritic cells (DCs) to present antigen to CD4+ and CD8+ T cells.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.