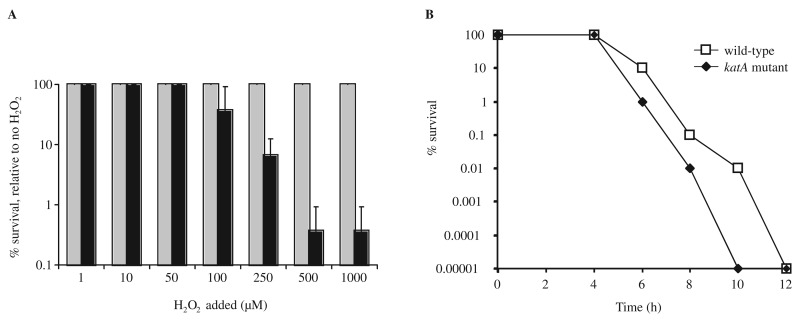
Fig. 3.
The H. hepaticus catalase is required for resistance to hydrogen peroxide and contributes to aerotolerance. (A) H. hepaticus peroxide sensitivity was measured by incubating strain ATCC 51449 (gray bars) and its isogenic katA mutant (black bars) in PBS supplemented with H2O2 concentrations ranging from 0 to 1000 mM. Survival of cells was monitored by spotting 10-fold dilutions on Dent plates, and visual assessment of growth after 2 days. Survival is expressed as percentage of the cfu count of the wild-type strain or katA mutant in PBS without H2O2 supplementation. The wild-type strain did not show any killing by H2O2 at these concentrations, whereas the katA mutant showed decreased survival at H2O2 concentrations exceeding 100 µM. Data shown are the average of three independent experiments, and error bars denote standard deviation. (B) Inactivation of katA reduces aerotolerance of H. hepaticus. Aerotolerance of H. hepaticus wild-type strain (open squares) and its isogenic katA mutant (black diamonds) was determined by exposing half of an overnight culture to atmospheric oxygen conditions [15, 26]. Survival of cells was monitored by plating 10-fold dilutions on Dent plates, and is expressed as percentage of the other half of the culture incubated microaerobically. Data shown are from a single experiment, representative for the three experiments performed