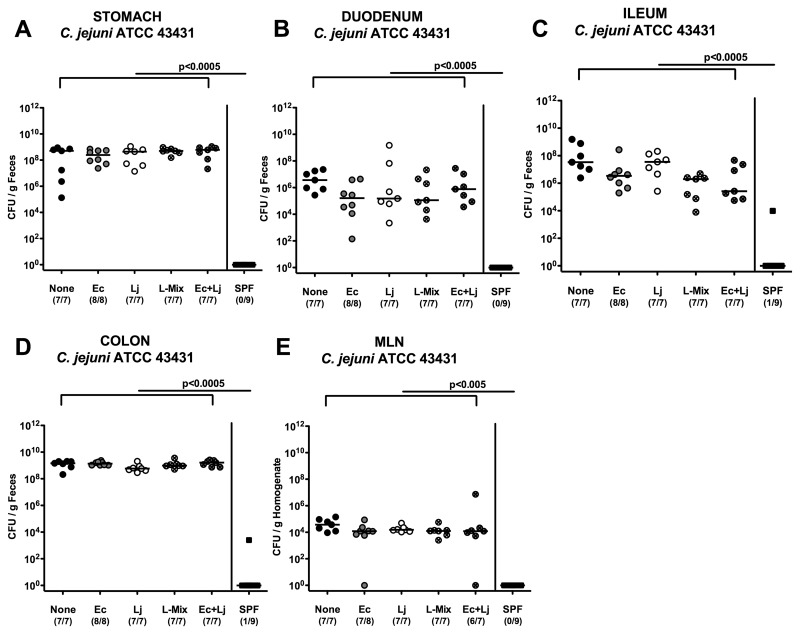
Fig. 1.
C. jejuni colonization along the gastrointestinal tract and translocation into MLNs of defined recolonized gnotobiotic mice. Gnotobiotic mice were generated by antibiotic gut decontamination, recolonized with E. coli (Ec, gray circles), Lactobacillus johnsonii (Lj, white circles), a Lactobacilli-mix (L-mix, crossed circles), a mix of E. coli and L. johnsonii (Ec+Lj, crossed gray circles), sterile PBS (none, solid circles), or a complex conventional murine SPF microbiota (solid squares), and orally infected with C. jejuni strain ATCC 43431 as described in the section titled Materials and methods. The pathogen densities in distinct compartments of the gastrointestinal tract (A–D) and mesenteric lymph nodes (MLNs, E) were determined by quantification of live C. jejuni in luminal samples taken from (A) stomach, (B) duodenum, (C) ileum, and (D) colon at day 12 p.i. by cultural analysis (CFU, colony forming units). Numbers of animals harboring C. jejuni out of the total number of analyzed animals are given in parentheses. Medians (black bars) and levels of significance (P-values) determined by Mann–Whitney-U test are indicated. Data shown are representative for three independent experiments