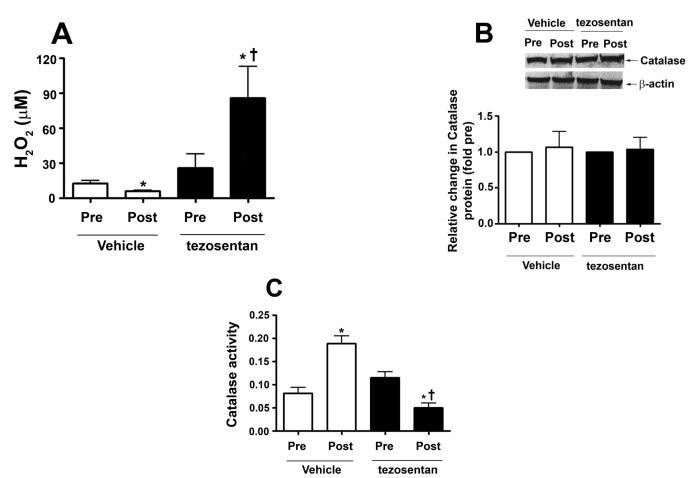
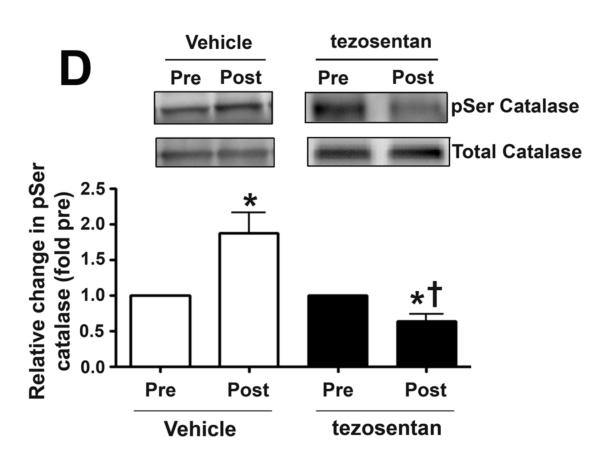
Figure 5. ET receptor antagonism increases lung tissue H2O2 levels, in association with attenuated catalase activity, in lambs acutely exposed to increased pulmonary blood flow.
Lung biopsies were taken before (Pre) and 4h after (Post) the increase in PBF. In vehicle-treated lambs, H2O2 levels, as estimated by H2DCFDA oxidation, decreased after 4h of increased PBF; whereas, in tezosentan-treated lambs, H2O2 levels increased (A). Western blot analysis performed on lysates (20μg) prepared from Pre and Post lung biopsies, revealed no change in catalase protein after 4h of increased PBF, in either vehicle- or tezosentan-treated lambs (B). However, in vehicle-treated lambs, lung tissue catalase activity was enhanced after 4h of PBF; whereas, in tezosentan-treated lambs catalase activity decreased (C). Lung lysate (1 mg) were also subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP), using an antibody specific to catalase followed by Western blot (IB) analysis using a specific antiserum raised against phosphorylated-serine residues. In vehicle-treated lambs, the increase in catalase activity was associated with an increase in phospho-serine catalase (pSercatalase), whereas, in tezosentan treated lambs pSer-catalase levels were decreased (D). Data are mean ± SEM; n =5-7. *P <0.05 vs. pre shunt opening, †P <0.05 vs. vehicle-treated post.