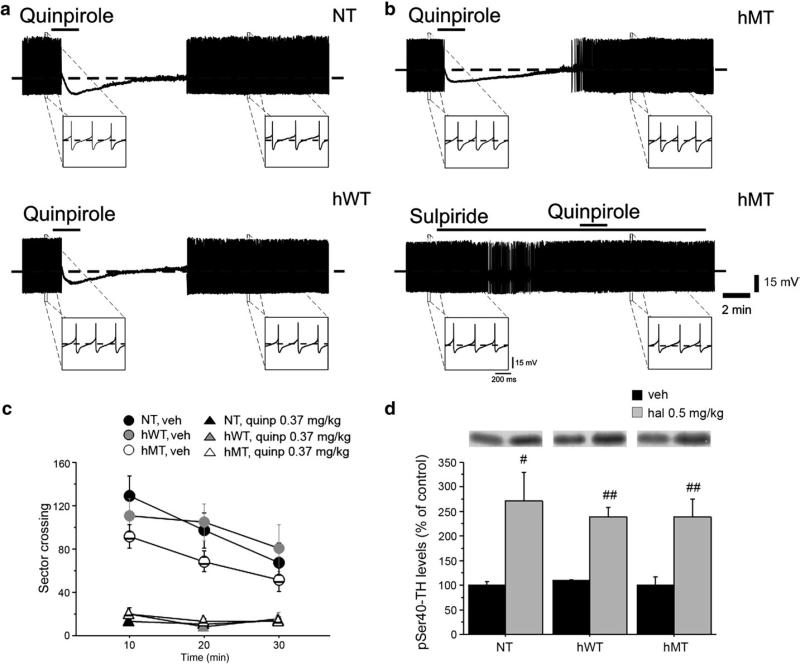
Fig. 1.
Unaltered DA D2R-mediated autoreceptor function in hMT mice. Representative traces showing the effects of quinpirole (10 μM, 2 min) on nigral dopaminergic neurons. Bath-applied quinpirole hyperpolarizes the cell membrane and abolishes the spontaneous firing activity of neurons recorded from NT (a, upper trace), hWT (a, lower trace) and hMT slices (b, upper trace). Note that the D2R agonist elicits similar responses in the three groups of mice. Upon quinpirole washout, the membrane slowly returns to pre-drug level and firing activity is resumed. The quinpirole effect is prevented by pretreatment of the slice with the D2R antagonist sulpiride (3 μM) (b, lower trace), confirming the specificity of the response to quinpirole. (c) Quinpirole induced motor suppression in all genotypes. Locomotor activity, expressed as number of sector crossing (mean ± SEM), has been measured each 10 min over a total 30 min test. Mice were injected i.p. with vehicle (NT n = 11, hWT n = 9, hMT n = 18) or quinpirole 0.35 mg/kg (NT n = 20, hWT n = 11, hMT n = 14) immediately before the test. (d) Haloperidol increased phosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) at Ser40 in all groups tested. Mice were injected i.p. with vehicle (n = 6, each genotype) or haloperidol 0.5 mg/kg (NT n = 7, hWT n = 7, hMT n = 6) and killed 15 min later to perform western blotting analysis of striatal pSer40-TH. Upper panels show representative autoradiograms. Lower panels show summary of density values, normalized to DARPP32 and expressed as mean ± SEM. Genotypes and treatments are as indicated. veh: vehicle, quinp: quinpirole. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, compared with vehicle group, within genotypes.