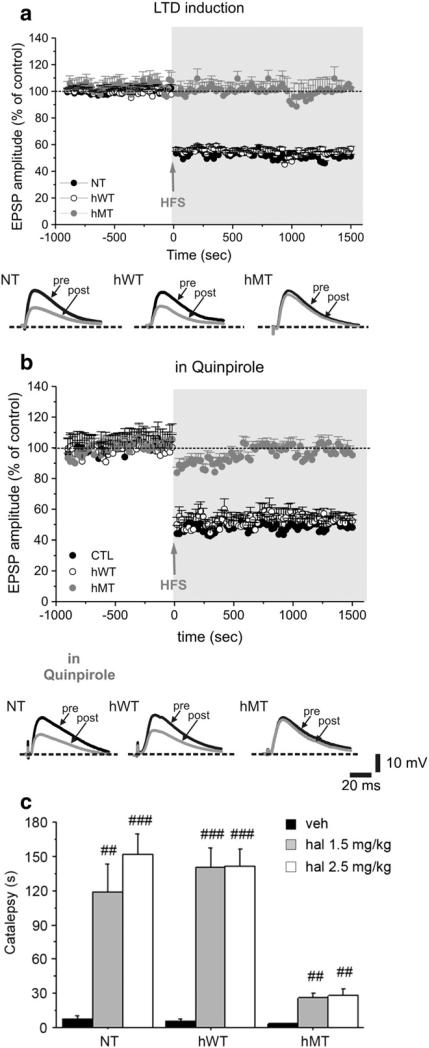
Fig. 2.
Impaired D2R-dependent postsynaptic function in hMT mice. Time-course of LTD induction in striatal medium spiny neurons from NT mice, hWT and hMT mice. (a) High-frequency stimulation (HFS, arrow) induces a robust LTD both in NT (filled circles) and hWT (open circles) mice, but not in hMT mice (grey circles). Representative traces of EPSPs recorded before (pre) and 20 min after (post) HFS in the three groups of mice. (b) Pretreatment of the slices with the D2R agonist quinpirole (10 μM, 20 min) does not modify the time-course of LTD in NT and hWT mice, nor it rescues LTD in hMT mice. Below, sample EPSPs are shown, measured before (pre) and 20 min after HFS (post). (c) Haloperidol induced a reduced cataleptic response in hMT animals. Mice were injected i.p. with vehicle (n = 8, each genotype), haloperidol 1.5 mg/kg (NT n = 8, hWT n = 8, hMT=7) or haloperidol 2.5 mg/kg (NT n = 8, hWT n = 8, hMT=7). Catalepsy time (s) was measured 120 min after injection. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Genotypes and treatments are as indicated. veh: vehicle, haloperidol: hal. ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.0001, compared with vehicle group, within genotype; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 compared with NT mice at the corresponding dose.