Fig 6.
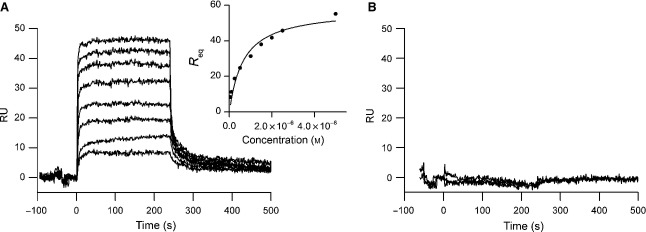
Interaction of promyostatin with immobilized WFIKKN1 and WFIKKN2. (A) Sensorgrams of the interactions of promyostatin (50, 100, 250, 500, 1000, 1500, 2000, and 2500 nm) with WFIKKN1. (B) Sensorgrams of the interactions of promyostatin (100, 500, and 2000 nm) with WFIKKN2. Various concentrations of promyostatin in 20 mm Hepes, 150 mm NaCl, 5 mm EDTA and 0.005% Tween-20 (pH 7.5) were injected over CM5 sensorchips containing immobilized WFIKKN1 or WFIKKN2. For the sake of clarity, the concentrations of promyostatin are not indicated in the panels; in (A), the SPR response increased in parallel with the increase of promyostatin concentration. In (A), the inset shows the equilibrium responses plotted against the concentration of injected promyostatin; the equilibrium dissociation constant was determined by fitting the curve with the general fitting model ‘Steady state affinity’ of biaevaluation 4.1. The equilibrium dissociation constant of the interaction of promyostatin with WFIKKN1 was ∼ 1 × 10−6 m. RU - SPR Response Units.
