Figure 10.
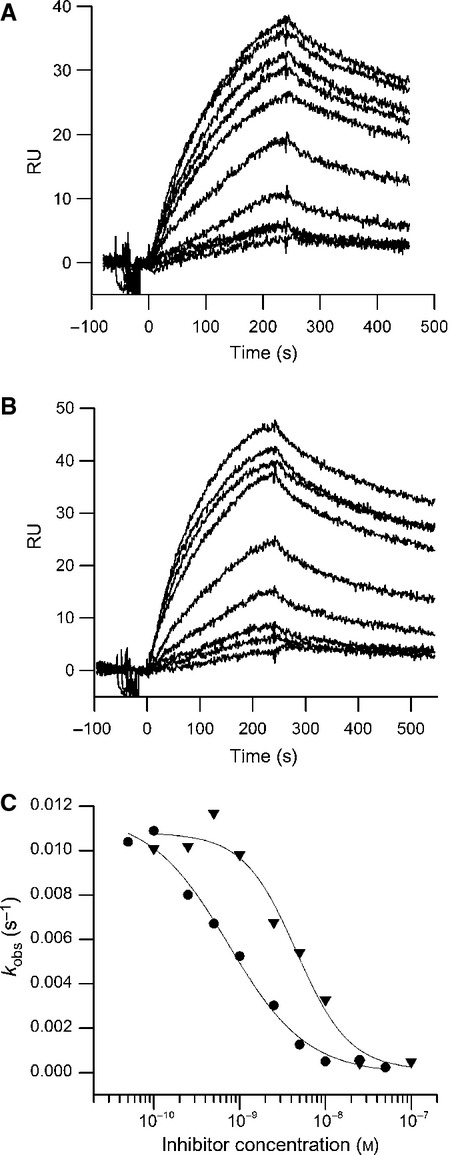
WFIKKN1 and WFIKKN2 inhibit the binding of latent myostatin to ECD_ACRIIB. (A) Sensorgrams of the interactions of immobilized ECD_ACRIIB with 500 nm latent myostatin preincubated with WFIKKN1 (0, 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2.5, 5, 10, 25, and 50 nm). (B) Sensorgrams of the interactions of immobilized ECD_ACRIIB with 500 nm latent myostatin preincubated with WFIKKN2 (0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2.5, 5, 10, 25, 50, and 100 nm). For the sake of clarity, the concentrations of WFIKKNs are not indicated in the panels; the SPR response decreased in parallel with the increase in WFIKKN concentration. (C) Values of the apparent association constant kobs from (A) and (B) were plotted against WFIKKN1 (▼) and WFIKKN2 (•) concentrations. Note that kobs values decreased with the increase in WFIKKN1 or WFIKKN2 concentration; half-maximal inhibition was achieved with ∼ 1 × 10−9 m WFIKKN1 or ∼ 5 × 10−9 m WFIKKN2. In these experiments, various concentrations of WFIKKN1 or WFIKKN2 were preincubated with latent myostatin in 20 mm Hepes, 150 mm NaCl, 5 mm EDTA and 0.005% Tween-20 (pH 7.5) for 30 min at room temperature, and were injected over CM5 sensorchips containing immobilized ECD_ACRIIB. RU - SPR Response Units.
