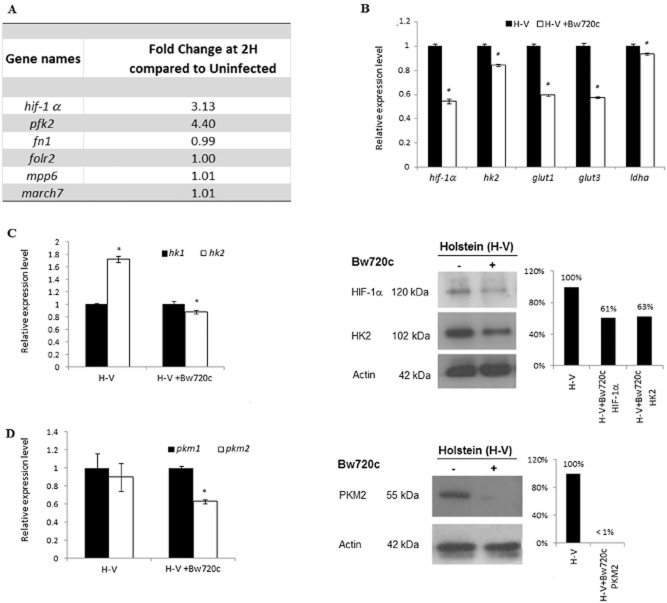
Figure 1.
In Holstein-Friesian infected leukocytes HIF-1α activation is parasite-dependent and leads to upregulated expression of HIF-1α target genes.A. Holstein-Friesian (H)-derived resting peripheral monocytes were infected in vitro with T. annulata sporozoites and RNA was isolated and used to probe a bovine macrophage microarray. At 2 h post infection hif-1α transcript levels are threefold higher in infected cells compared with non-infected monocytes. The HIF-1α-target gene pfk2 is upregulated fourfold, whereas 80% of genes show no change, including fn1, folr2, mpp6 and march7.B. In virulent (H-V) macrophages the transcription levels of hif-1α and a selection of its target genes (glut1, glut3, pdk1, ldha and hk2) diminishes upon Bw720c-induced parasite death. *Student’s t-test, highest P-value = 0.0482 < 0.05.C. Bw720c-induced parasite death in H-V macrophages leads to a drop in hk2 transcripts and a reduction in both HIF-1α and HK2 levels. *Student’s t-test, highest P-value = 0.0358 < 0.05.D. PKM2 expression also drops upon Bw720c-induced parasite death. The amount of actin expressed was used as a loading control. *Student’s t-test, P-value = 0.0376 < 0.05.