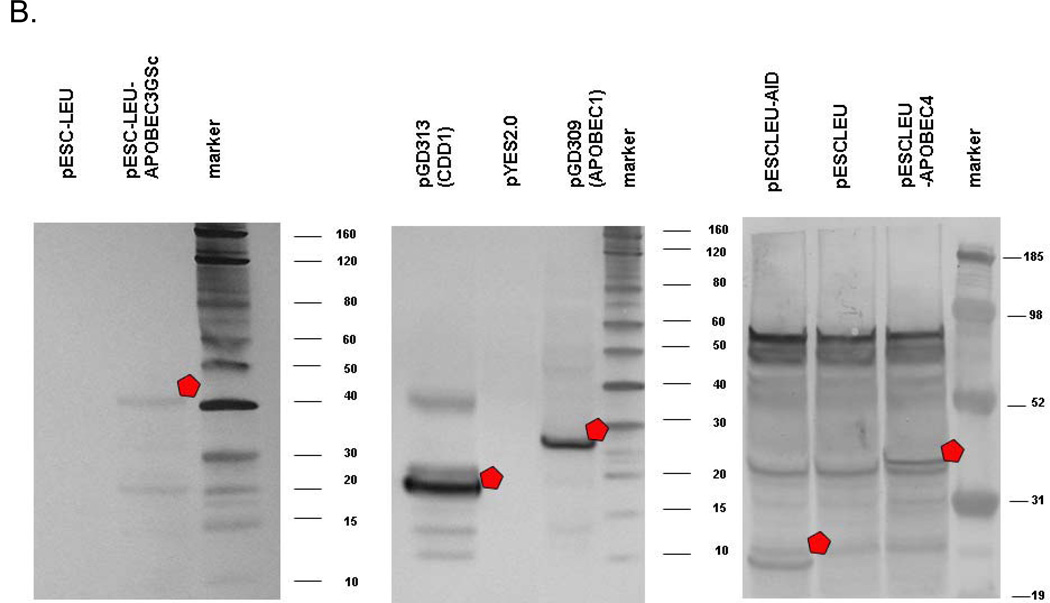
Fig. 5.
Detection of AID/CDD1/APOBEC proteins in extracts. a) Production of deaminases in bacteria. Proteins in bacterial extracts were separated on 12% polyacrylamide gels and stained by Coomassie G-450. Lanes: M, molecular weight marker; S, supernatant of the protein extract; P, protein extract pellet prepared as described in “Materials and Methods”. Predicted molecular weights are for 27.2 kDa for PmCDA1-His6, 47.2 kDa for APOBEC3G, 17.7 kDa for APOBEC5-His6, 29.4 kDa for His6-Tad2, and 39.4 kDa for Tad3-S-tag. b) Production of deaminases in yeast. The results of Western blots are shown. Proteins of correct size are marked by a white pentagon. Protein in yeast extracts of appropriate strains were separated using 4–12% gradient polyacrylamide gel (Invitrogen). Transfer to PVDF membrane and reaction with appropriate primary antibodies from mouse and then secondary antibodies from goat was accomplished as suggested by the vendor (Western Breeze kit; Invitrogen). Primary antibodies were mouse anti c-myc for tagged hApobec3G, anti-FLAG for tagged APOBEC4, monoclonal anti-HA for tagged APOBEC1 and CDD1.