Abstract
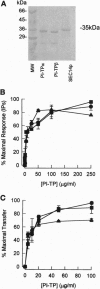
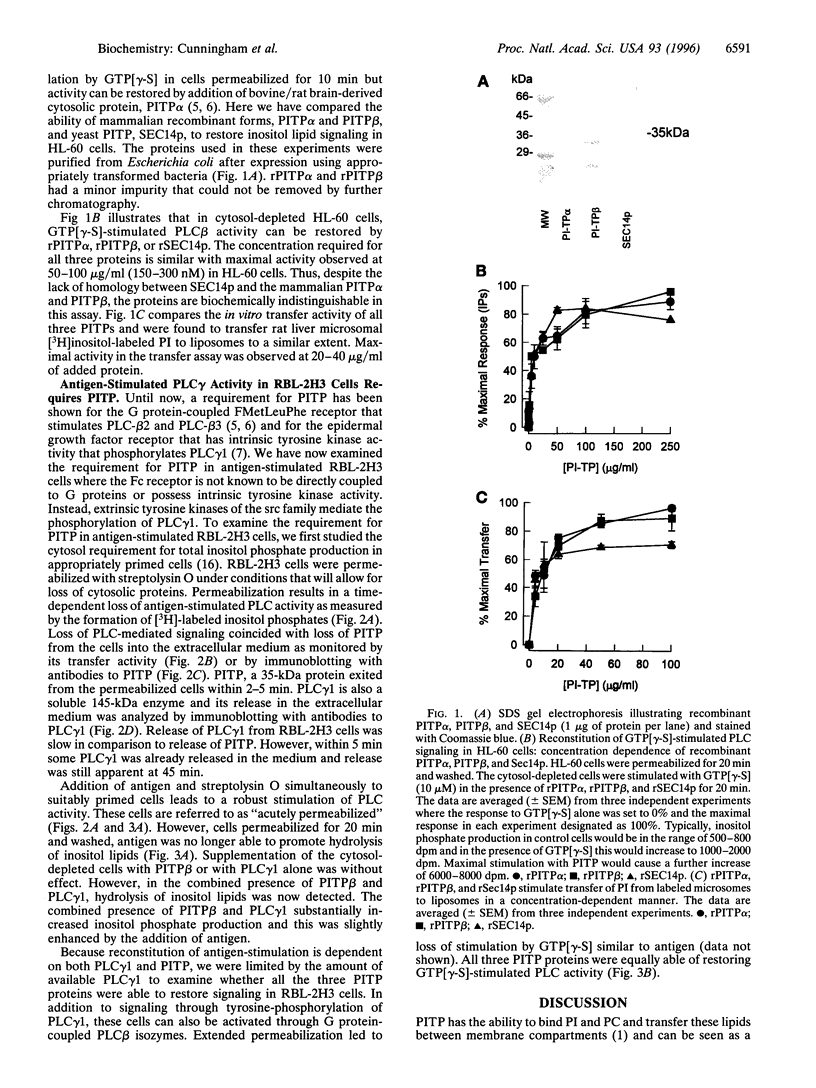
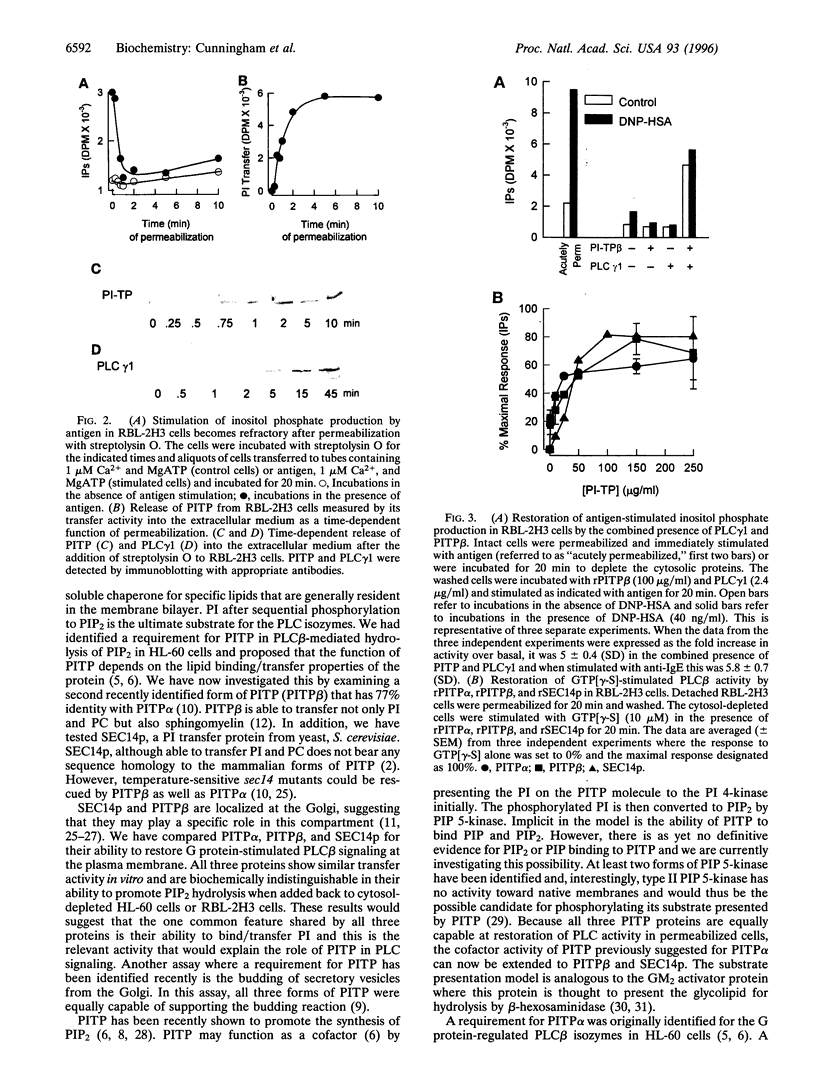
The mammalian phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins (PITP) and the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae PITP (SEC14p) that show no sequence homology both catalyze exchange of phosphatidylinositol (PI) between membranes compartments in vitro. In HL-60 cells where the cytosolic proteins are depleted by permeabilization, exogenously added PITPalpha is required to restore G protein-mediated phospholipase Cbeta (PLCbeta) signaling. Recently, a second mammalian PITPbeta form has been described that shows 77% identity to rat PITPalpha. We have examined the ability of the two mammalian PITPs and SEC14p to restore PLC-mediated signaling in cytosol-depleted HL-60 and RBL-2H3 cells. Both PITPalpha and PITPbeta isoforms as well as SEC14p restore G protein-mediated PLCbeta signaling with a similar potency. In RBL-2H3 cells, crosslinking of the IgE receptor by antigen stimulates inositol lipid hydrolysis by tyrosine phosphorylation of PLCgamma1. Permeabilization of RBL cells leads to loss of PLCgamma1 as well as PITP into the extracellular medium and this coincides with loss of antigen-stimulated lipid hydrolysis. Both PLCgamma1 and PITP were required to restore inositol lipid signaling. We conclude that (i) because the PI binding/transfer activities of PITP/SEC14p is the common feature shared by all three transfer proteins, it must be the relevant activity that determines their abilities to restore inositol lipid-mediated signaling and (ii) PITP is a general requirement for inositol lipid hydrolysis regardless of how and which isoform of PLC is activated by the appropriate agonist.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali H., Cunha-Melo J. R., Beaven M. A. Receptor-mediated release of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,4-bisphosphate in rat basophilic leukemia RBL-2H3 cells permeabilized with streptolysin O. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 17;1010(1):88–99. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90188-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali H., Cunha-Melo J. R., Saul W. F., Beaven M. A. Activation of phospholipase C via adenosine receptors provides synergistic signals for secretion in antigen-stimulated RBL-2H3 cells. Evidence for a novel adenosine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):745–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson T. P., Kaliner M. A., Hohman R. J. Phospholipase C-gamma 1 is translocated to the membrane of rat basophilic leukemia cells in response to aggregation of IgE receptors. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2194–2200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankaitis V. A., Aitken J. R., Cleves A. E., Dowhan W. An essential role for a phospholipid transfer protein in yeast Golgi function. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):561–562. doi: 10.1038/347561a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankaitis V. A., Malehorn D. E., Emr S. D., Greene R. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae SEC14 gene encodes a cytosolic factor that is required for transport of secretory proteins from the yeast Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1271–1281. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazenet C. E., Ruano A. R., Brockman J. L., Anderson R. A. The human erythrocyte contains two forms of phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase which are differentially active toward membranes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):18012–18022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchini L., Todderud G., Grinstein S. Cytosolic [Ca2+] homeostasis and tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C gamma 2 in HL60 granulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3357–3363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake R. A., Walker T. R., Watson S. P. Activation of human platelets by peroxovanadate is associated with tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C gamma and formation of inositol phosphates. Biochem J. 1993 Mar 1;290(Pt 2):471–475. doi: 10.1042/bj2900471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleves A. E., McGee T. P., Whitters E. A., Champion K. M., Aitken J. R., Dowhan W., Goebl M., Bankaitis V. A. Mutations in the CDP-choline pathway for phospholipid biosynthesis bypass the requirement for an essential phospholipid transfer protein. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):789–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90508-v. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Thomas G. M., Cunningham E., Ball A. Use of cytosol-depleted HL-60 cells for reconstitution studies of G-protein-regulated phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C-beta isozymes. Methods Enzymol. 1994;238:154–168. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(94)38014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham E., Thomas G. M., Ball A., Hiles I., Cockcroft S. Phosphatidylinositol transfer protein dictates the rate of inositol trisphosphate production by promoting the synthesis of PIP2. Curr Biol. 1995 Jul 1;5(7):775–783. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00154-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickeson S. K., Helmkamp G. M., Jr, Yarbrough L. R. Sequence of a human cDNA encoding phosphatidylinositol transfer protein and occurrence of a related sequence in widely divergent eukaryotes. Gene. 1994 May 16;142(2):301–305. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90279-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiseman E., Bolen J. B. Engagement of the high-affinity IgE receptor activates src protein-related tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):78–80. doi: 10.1038/355078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst W., Sandhoff K. Activator proteins and topology of lysosomal sphingolipid catabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jun 5;1126(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(92)90210-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. E., Hajduk P. J., Yoon H. S., Fesik S. W. Pleckstrin homology domains bind to phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate. Nature. 1994 Sep 8;371(6493):168–170. doi: 10.1038/371168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay J. C., Fisette P. L., Jenkins G. H., Fukami K., Takenawa T., Anderson R. A., Martin T. F. ATP-dependent inositide phosphorylation required for Ca(2+)-activated secretion. Nature. 1995 Mar 9;374(6518):173–177. doi: 10.1038/374173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay J. C., Martin T. F. Phosphatidylinositol transfer protein required for ATP-dependent priming of Ca(2+)-activated secretion. Nature. 1993 Dec 9;366(6455):572–575. doi: 10.1038/366572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffmann-Zeh A., Thomas G. M., Ball A., Prosser S., Cunningham E., Cockcroft S., Hsuan J. J. Requirement for phosphatidylinositol transfer protein in epidermal growth factor signaling. Science. 1995 May 26;268(5214):1188–1190. doi: 10.1126/science.7761838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier E. M., Schwarzmann G., Fürst W., Sandhoff K. The human GM2 activator protein. A substrate specific cofactor of beta-hexosaminidase A. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1879–1887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi M., Jan de Vries K., Frank R., Snoek G., Bankaitis V., Wirtz K., Huttner W. B. A role for phosphatidylinositol transfer protein in secretory vesicle formation. Nature. 1995 Oct 12;377(6549):544–547. doi: 10.1038/377544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa K., Szallasi Z., Kazanietz M. G., Blumberg P. M., Mischak H., Mushinski J. F., Beaven M. A. Ca(2+)-dependent and Ca(2+)-independent isozymes of protein kinase C mediate exocytosis in antigen-stimulated rat basophilic RBL-2H3 cells. Reconstitution of secretory responses with Ca2+ and purified isozymes in washed permeabilized cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1749–1756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park D. J., Min H. K., Rhee S. G. IgE-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 in rat basophilic leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24237–24240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Hemmings B. A., Gierschik P. PH domains and phospholipases--a meaningful relationship? Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Feb;19(2):54–55. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90031-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Kinet J. P. Fc receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:457–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.002325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Ryu S. H., Lee K. Y., Cho K. S. Assays of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C and purification of isozymes from bovine brains. Methods Enzymol. 1991;197:502–511. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)97176-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiue L., Green J., Green O. M., Karas J. L., Morgenstern J. P., Ram M. K., Taylor M. K., Zoller M. J., Zydowsky L. D., Bolen J. B. Interaction of p72syk with the gamma and beta subunits of the high-affinity receptor for immunoglobulin E, Fc epsilon RI. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jan;15(1):272–281. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.1.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner H. B., Alb J. G., Jr, Whitters E. A., Helmkamp G. M., Jr, Bankaitis V. A. Phospholipid transfer activity is relevant to but not sufficient for the essential function of the yeast SEC14 gene product. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4775–4784. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06166.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner H. B., McGee T. P., McMaster C. R., Fry M. R., Bell R. M., Bankaitis V. A. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae phosphatidylinositol-transfer protein effects a ligand-dependent inhibition of choline-phosphate cytidylyltransferase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 3;92(1):112–116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.1.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snoek G. T., de Wit I. S., van Mourik J. H., Wirtz K. W. The phosphatidylinositol transfer protein in 3T3 mouse fibroblast cells is associated with the Golgi system. J Cell Biochem. 1992 Aug;49(4):339–348. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240490404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Hosaka K. Cloning of a cDNA encoding a second phosphatidylinositol transfer protein of rat brain by complementation of the yeast sec14 mutation. J Biochem. 1994 May;115(5):981–984. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a124448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. M., Cunningham E., Fensome A., Ball A., Totty N. F., Truong O., Hsuan J. J., Cockcroft S. An essential role for phosphatidylinositol transfer protein in phospholipase C-mediated inositol lipid signaling. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):919–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90471-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerman J., de Vries K. J., Somerharju P., Timmermans-Hereijgers J. L., Snoek G. T., Wirtz K. W. A sphingomyelin-transferring protein from chicken liver. Use of pyrene-labeled phospholipid. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 16;270(24):14263–14266. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.24.14263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirtz K. W. Phospholipid transfer proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:73–99. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.000445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K., Jelsema C. L., Beaven M. A. Certain inhibitors of protein serine/threonine kinases also inhibit tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C gamma 1 and other proteins and reveal distinct roles for tyrosine kinase(s) and protein kinase C in stimulated, rat basophilic RBL-2H3 cells. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 1;149(3):1031–1037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries K. J., Heinrichs A. A., Cunningham E., Brunink F., Westerman J., Somerharju P. J., Cockcroft S., Wirtz K. W., Snoek G. T. An isoform of the phosphatidylinositol-transfer protein transfers sphingomyelin and is associated with the Golgi system. Biochem J. 1995 Sep 1;310(Pt 2):643–649. doi: 10.1042/bj3100643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries K. J., Momchilova-Pankova A., Snoek G. T., Wirtz K. W. A novel acidic form of the phosphatidylinositol transfer protein is preferentially retained in permeabilized Swiss mouse 3T3 fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1994 Nov;215(1):109–113. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Paridon P. A., Gadella T. W., Jr, Somerharju P. J., Wirtz K. W. Properties of the binding sites for the sn-1 and sn-2 acyl chains on the phosphatidylinositol transfer protein from bovine brain. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 23;27(17):6208–6214. doi: 10.1021/bi00417a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]