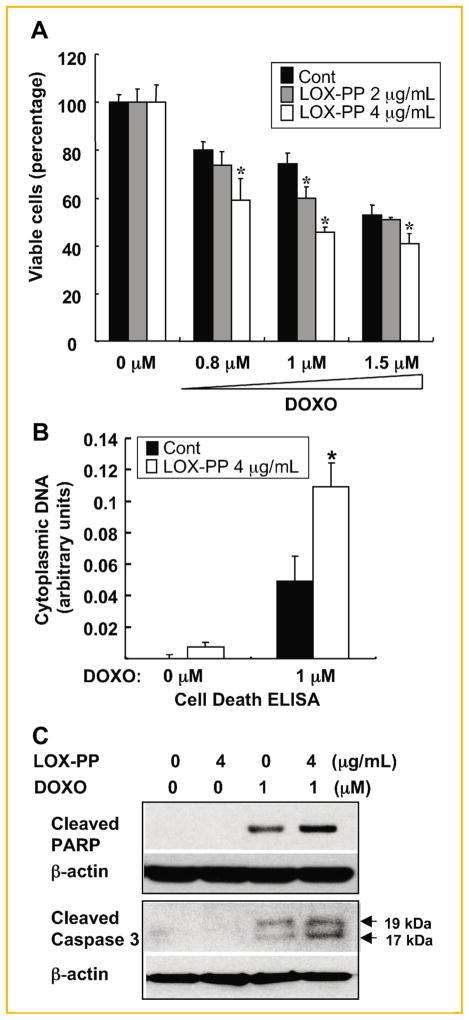
Fig. 3.
LOX-PP enhances doxorubicin-mediated killing of MIA PaCa-2 cells in culture. A: MIA PaCa-2 cells were pre-treated with 2 or 4 μg/ml LOX-PP or water as control in DMEM–2% CS-FBS for 24 h, and then the indicated amounts of doxorubicin were added for an additional 24 h. Cell viability was determined by measuring ATP production. The value obtained with 0 μM doxorubicin was set to 100%. Data represent mean ± SD of quadruplicate samples (these experiments have been repeated in a similar manner at least two times and data from a representative experiment shown). P values were calculated using Student’s t-test, *P <0.05. B: Cells were treated with 0 or 4 μg/ml LOX-PP for 24 h and then with 0 or 1 μM doxorubicin for an additional 24 h. Cell Death ELISA assays were performed as described in the Materials and Methods Section. Data represent mean ± SD of triplicate samples. P values were calculated using Student’s t-test. C: MIA PaCa-2 cells were treated either with doxorubicin (1 μM) or LOX-PP (4 μg/ml) individually or in combination as described above and WCEs analyzed by immunoblotting for cleaved PARP and caspase 3 expression, and for β-actin, which confirmed equal loading.