Figure 3.
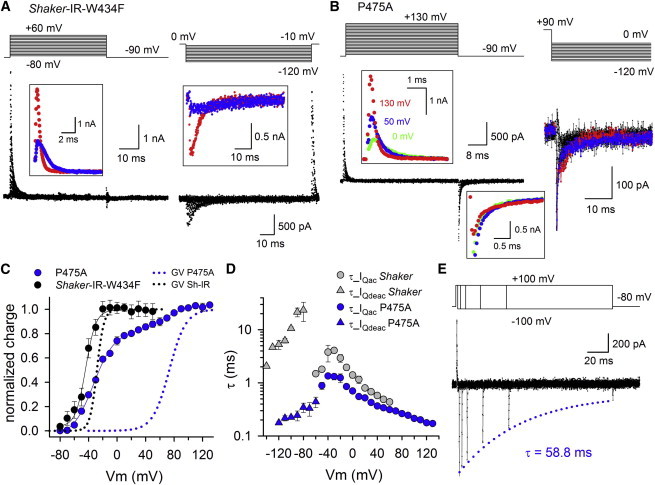
Gating current measurements of Shaker-IR-W434F and P475A. (A) Gating current recordings of Shaker-IR-W434F control obtained with activation (left) or a deactivation (right) protocol. On the left, a scaled up view of the activating gating currents (IQac) at +20 mV (blue) and +60 mV (red) are shown as inset. With increasing depolarization strengths the IQac kinetics accelerate causing the IQac tracings to cross each other. Inset on the right shows a scaled up view of the deactivating gating currents (IQdeac) at −90 mV (blue) and −120 mV (red). Similar to IQac, IQdeac decay accelerated with stronger repolarizations. (B) Representative IQac (left) and IQdeac (right) recordings of P475A. Insets show a scaled up view of both IQac and IQdeac obtained with the activation protocol. Similar to control (panel A), IQac accelerated with stronger depolarizations, which is highlighted by coloring the recordings at 0 mV (green), +50 mV (blue), and +130 mV (red). Scale up view of the IQdeac recordings at −90 mV shows that IQdeac did not slow down up to prepulse depolarizations of +50 mV in strength (note the overlap of the green and blue recording, which were obtained upon a 0 and +50 mV prepulse, respectively). However, upon a +130 mV prepulse (red trace) there was a reduction in IQdeac amplitude suggesting that the IQdeac kinetics were slowed down (larger scale of this scaled up view is shown in the Supporting Material). Right panel displays IQdeac recordings that were elicited with a deactivation pulse protocol by stepping after a 150-ms +90 mV prepulse to potentials between 0 and −120 mV. The blue and the red trace were obtained at −80 mV and −120 mV, respectively. (C) QV curves (symbols and line, which represent average fit with a single or sum of two Boltzmann distributions) of Shaker-IR-W434F (black) and P475A (blue) obtained by integrating and normalizing the IQac recordings. For comparison, the GV curves are represented in dotted lines. Note, the QV curve of P475A displayed two gating charge components whereby the first component matched the QV curve of Shaker-IR-W434F, whereas the second component was shifted by ∼ +95 mV and corresponded to the shift in the GV curve. (D) Voltage-dependency of the IQac (circles) and IQdeac (triangles) time constants ± SE for Shaker-IR-W434F (gray symbols, n = 8) and P475A (blue symbols, n = 6). (E) Envelope pulse protocol to determine in P475A the effect of prolonging the prepulse depolarization on the speed of IQdeac decay (τ_IQdeac), which was elicited by repolarizing to −100 mV. With longer depolarization times at +100 mV there was a gradual decrease in IQdeac amplitude, most likely because of a slowing down in τ_IQdeac. Approximating the decay in IQdeac amplitude with a single exponential function (blue dotted line) yielded a time constant of 58.8 ms in the represented recording.
