Abstract
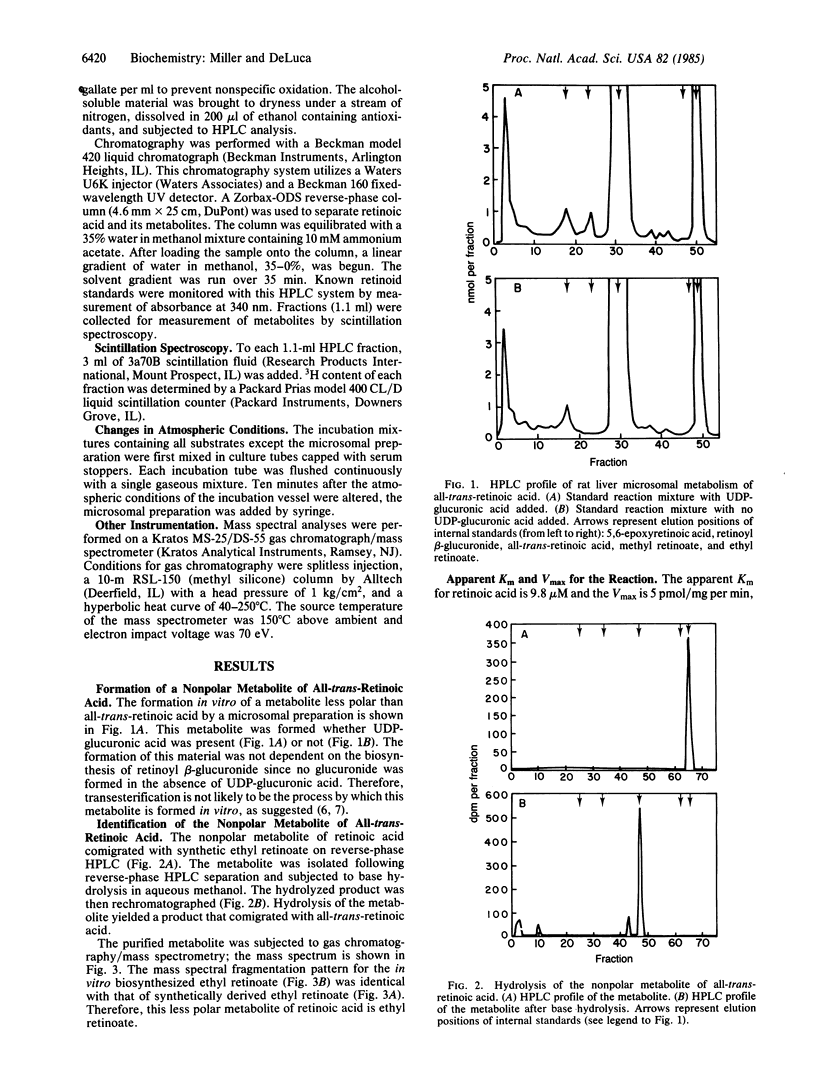
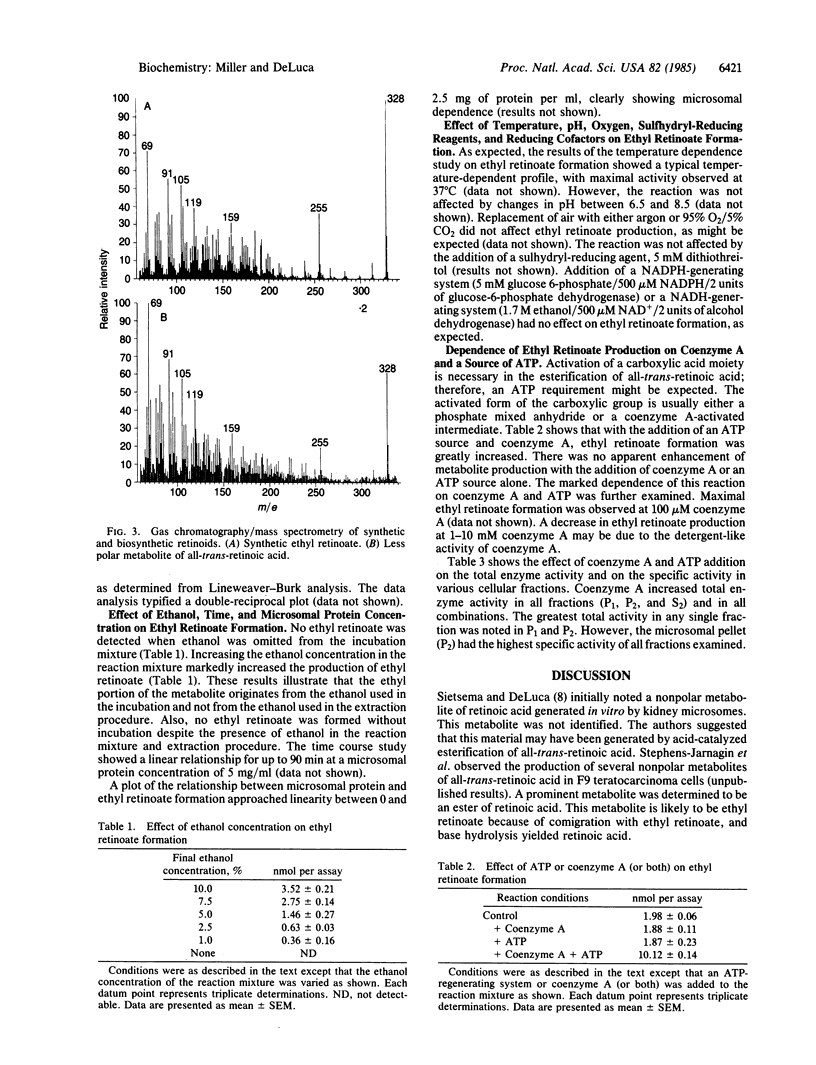
All-trans-retinoic acid is metabolized to a less polar metabolite in rat liver microsomes. This metabolite was proven to be ethyl retinoate by cochromatography on high-performance liquid chromatography, base hydrolysis to all-trans-retinoic acid, and gas chromatography/mass spectral analysis. The formation of ethyl retinoate is a specific enzymatic process; the apparent Km for all-trans-retinoic acid is 9.8 microM. The production of ethyl retinoate is greatly stimulated by the addition of coenzyme A, suggesting the formation of a retinoic acid-coenzyme A intermediate (retinoyl-coenzyme A).
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippel K., Olson J. A. Origin of some derivatives of retinoic acid found in rat bile. J Lipid Res. 1968 Sep;9(5):580–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sietsema W. K., DeLuca H. F. In vitro epoxidation of all-trans-retinoic acid in rat tissue homogenates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 29;90(4):1091–1097. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91147-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva D. P., Jr, DeLuca H. F. Metabolism of retinoic acid in vivo in the vitamin A-deficient rat. Biochem J. 1982 Jul 15;206(1):33–41. doi: 10.1042/bj2060033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skare K. L., Sietsema W. K., DeLuca H. F. The biological activity of retinotaurine. J Nutr. 1982 Aug;112(8):1626–1630. doi: 10.1093/jn/112.8.1626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens-Jarnagin A., Sietsema W. K., Miller D. A., DeLuca H. F. The biological activity of rat intestinal retinoic acid metabolites in the vaginal smear assay. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Feb 1;220(2):502–508. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90441-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zile M. H., Inhorn R. C., DeLuca H. F. Metabolites of all-trans-retinoic acid in bile: identification of all-trans- and 13-cis-retinoyl glucuronides. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3537–3543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


