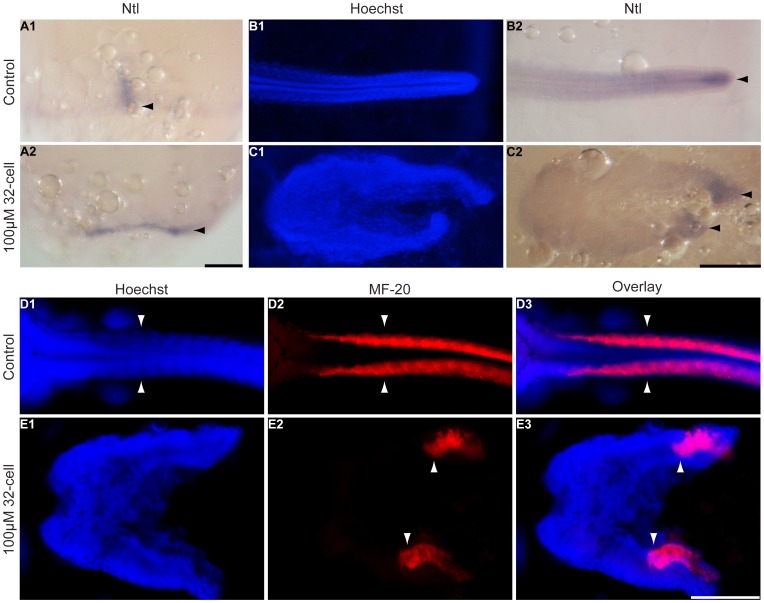
Figure 4. Somites and the notochord are divided in the splitbody phenotype.
K. marmoratus embryos were exposed to 100 µM dorsomorphin at the 32-cell stage and fixed 1 and 4 days post-fertilization in order to stain the notochord by in situ hybridization using a medaka ntl probe (A, B, C), and somites using the myosin antibody MF-20 (D, E). In control embryos at late gastrula, ntl stained axial mesoderm in the dorsal axis (A1 arrowhead, n = 10/10), whereas in DM treated embryos these cells appeared to have stayed in the lateral domains (A2 arrowhead, n = 10). At day 4, ntl stained the notochord in the tip of the tail for control embryos (B2 arrowhead, n = 10/10), whereas splitbody embryos had the tips of both body axes stained with ntl (C2 arrowheads, n = 10/10). For control embryos, somites are formed as pairs arranged either side of the neural axis (D1–3 arrowheads, n = 10/10). In the splitbody phenotype, somites were unpaired and separated in the two body axes (E1 Hoechst staining showing the body split; E2, 3 arrowheads, somites are present in both axes, n = 10/10). Photographs were taken at late gastrula for A, and 4 days post-fertilization for B–E. Images in A are lateral views and for B–E dorsal views of the embryos. Scale bars: 250 µm.