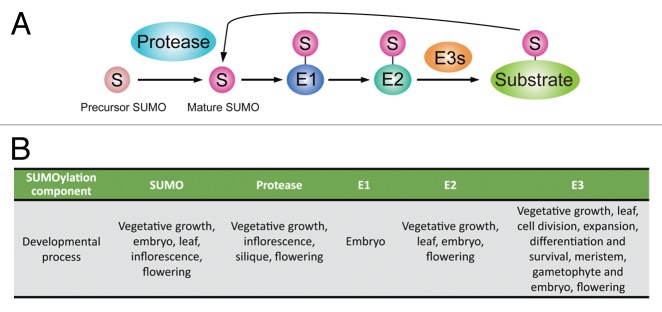
Figure 1. The SUMOylation pathway and its role in plant development. (A) The mechanism of reversible SUMOylation. SUMO is translated into a precursor form and SUMO proteases cleave SUMO into its mature form. Mature SUMO is conjugated to substrate in an ATP-dependent manner in reactions that are catalyzed by three enzymes, E1, E2 and E3, in sequence. SUMOylation is reversible and SUMO deconjugate from the substrate is catalyzed by the SUMO proteases involved in the maturation step. (B) SUMOylation regulates many aspects of developmental processes in plant.
