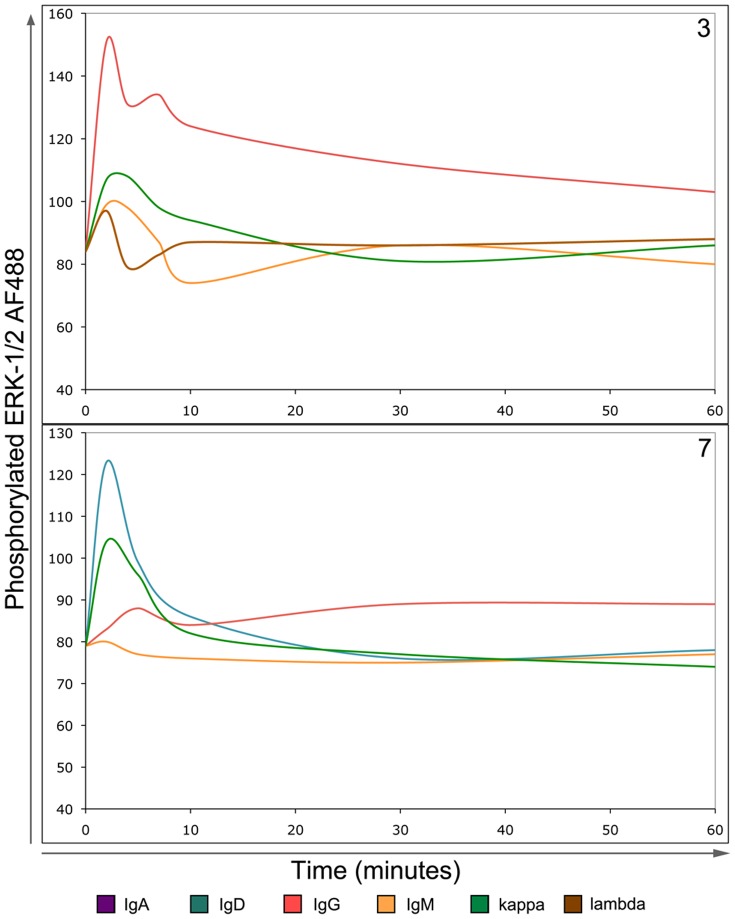
Figure 2. BCR-induced signals trigger phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in mult-HCL.
The BD phosflow assay system was used to measure phosphorylation of ERK1/2 following BCR stimuli. Cells were stimulated using goat F(ab’)2 anti-Ig antibodies for indicated times, fixed, permeabilised and CD19HICD11cHI lymphocytes examined for intensity of phosphorylated ERK1/2 staining. Patterns of ERK1/2 phosphorylation reflected induced calcium flux. Two representative examples are shown. Upper Panel: In IgD−ve mult-HCL Case 3 anti-IgG or κ stimuli induce Ca2+ flux and ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Notably, sIgM shown not to induce Ca2+ flux did not trigger ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Lower panel: In IgD+ mult-HCL Case 7, ERK1/2 phosphorylation patterns again reflected Ca2+ flux, both in intensity and type of signal. For example IgG-induced calcium flux was of low intensity and slow (Table 1), which is mirrored by the ERK1/2 phosphorylation kinetics observed. Both panels: Note that at early time points (1–2 minutes) a non-specific response is commonly observed in response to addition of antibody, as can be seen with anti-IgM and anti-λ negative controls in Case 3.