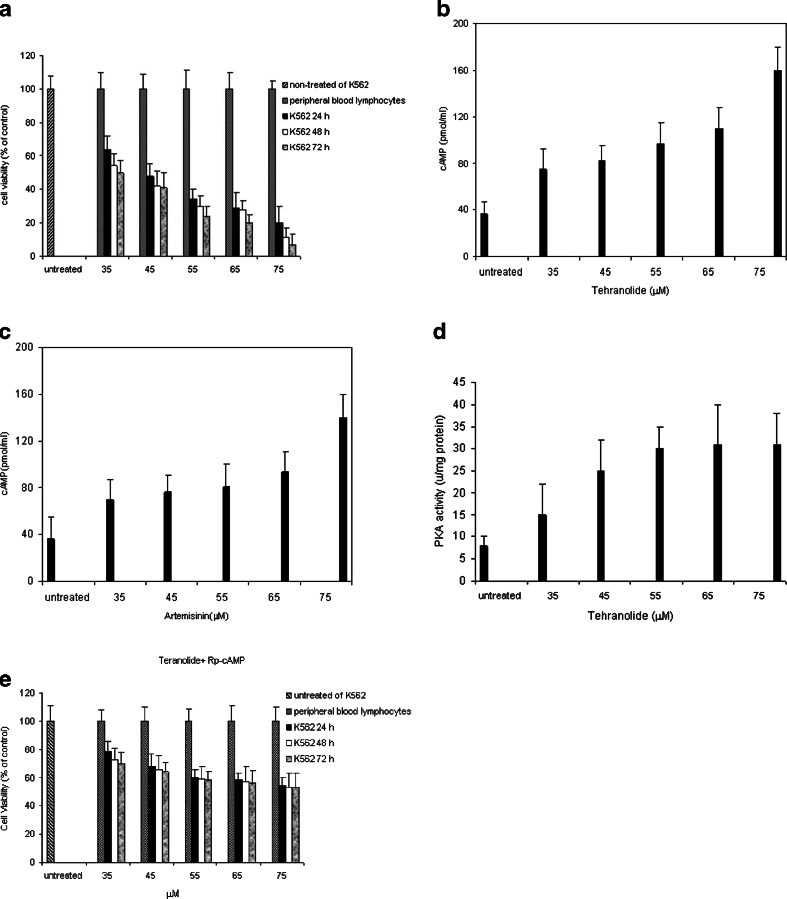
Fig. 5.
a Cytotoxicity effect of tehranolide against of K562 cell line. Cells were incubated with increasing concentrations (35–75 μM) of tehranolide for 24, 48, and 72 h Cell viability was quantified by applying the MTT assay. Bars represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments performed in triplicate, p < 0.05 represents significant differences compared to control values, whereby control was set as 100 %. b Intracellular levels of cAMP in tehranolide-treated K562 cells. K562 cells were treated with varying concentrations of tehranolide followed by analysis of intracellular cAMP levels. c Intracellular levels of cAMP in artemisinin-treated K562 cells. d PKA activity in tehranolide-treated K562 cells. PKA activity was determined using the Pierce colorimetric assay kit that utilizes a fluorescent-labeled kempeptide (a PKA-specific peptide (LRRASLG) substrate). e RpcAMP, a specific inhibitor of cAMP-dependent protein kinase A, inhibits PKA activation induced by cAMP. To detect the role of PKA activity on cell proliferation, cells were pretreated with RpcAMP(10 μM) for 20 min and then treated with different concentrations of tehranolide and harvested at 24, 48, and 72 h. Significant differences (p < 0.05) were found compared with untreated cells. The results are representative of three separate experiments