Fig. 7.
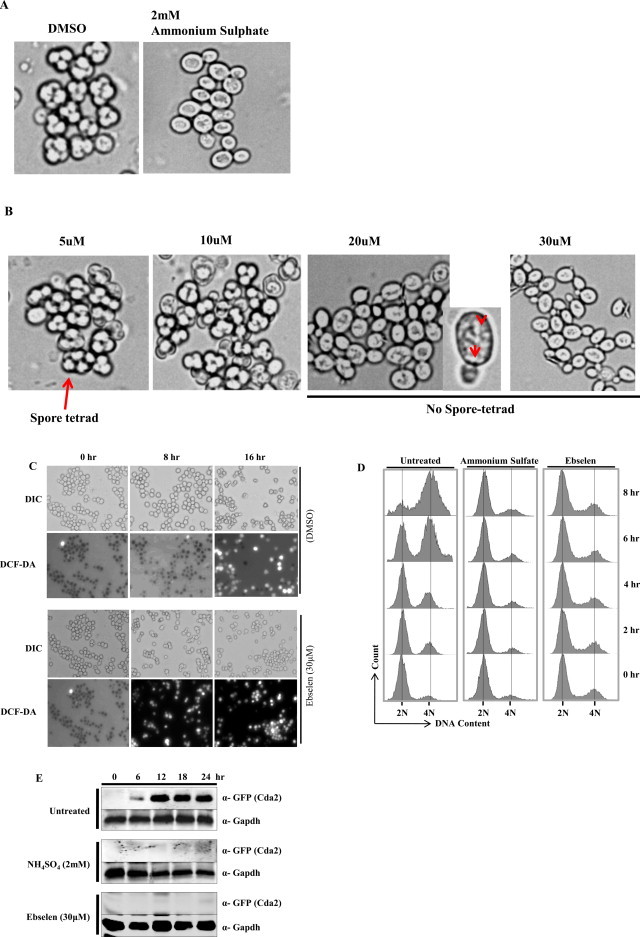
Ebselen strongly inhibits sporulation in yeast. (A) Microscopic images of cells sporulated for 24 h in the absence of drug (control), in the presence of 2 mM ammonium sulfate, (B) or increasing concentration of ebselen. Part of the 20 μM ebselen treated image was magnified; arrows indicate granular bodies of unknown origin. (C) Microscopic images of cells sporulated for indicated time (0, 8 and 16 h) in the absence of drug (DMSO), in the presence of 30 μM ebselen. The upper panels show phase contrast microscopy; the lower panels show fluorescence microscopy of the same cells after staining with DCF-DA. (D) Analysis of pre-meiotic DNA synthesis in a control (DMSO), and cells treated with ammonium sulfate (2 mM) or Ebselen (30 μM) through FACS. Samples were taken at regular interval as indicated in figure after induction of sporulation. Samples were subjected to FACS analysis and results were processed with BD FACS Diva software. (E) Yeast strain USY613 (USY61+ pCDA2-eGFP::HygB) was cultured as described in materials and methods and treated with 30 μM of ebselen or 2 mM ammonium sulfate for 24 h. 10 ml cells were harvested at regular intervals (0, 6, 12, 18, 24 h). Whole cell extracts were prepared by TCA extraction method and samples were subjected to western blot anlaysis using indicated antibodies. Tbp and Gapdh served as loading controls.
