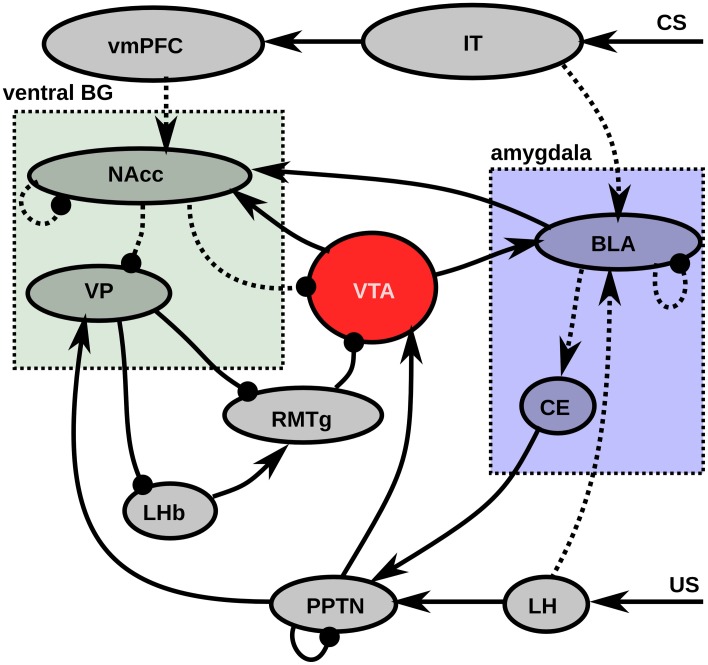
Figure 1.
Functional description of the model. Pointed arrows represent excitatory connections, rounded arrows represent inhibitory projections. Dashed lines represent learnable connections, while solid represent fixed connections. LH signals US delivery to BLA (Sah et al., 2003) and PPTN (Semba and Fibiger, 1992). IT encode a visual representation of the CS, which activates BLA (Cheng et al., 1997) and vmPFC (Carmichael and Price, 1995). BLA learns to associates the CS and US representations under the modulatory influence of the DA released by VTA (Bissière et al., 2003) and projects on CE (LeDoux, 2000) which excites PPTN (Semba and Fibiger, 1992). The excitatory projection from PPTN to VTA is able to provoke phasic DA bursts (Lokwan et al., 1999). NAcc MSN neurons receives excitatory projections from BLA (Ambroggi et al., 2008) and vmPFC (Haber, 2003) and learning is modulated by DA release from VTA (Robbins and Everitt, 1996). They inhibit VTA dopaminergic neurons (Usuda et al., 1998) and VP (Zahm and Heimer, 1990). VP also receives excitatory projections from PPTN (Hallanger and Wainer, 1988) and inhibits both LHb and RMTg (Haber and Knutson, 2010). LHb excites RMTg (Balcita-Pedicino et al., 2011) which in turn inhibits VTA (Jhou et al., 2009). Abbreviations: LH, lateral hypothalamus; IT, inferotemporal cortex; BLA, basolateral nucleus of the amygdala; CE, central nucleus of the amygdala; vmPFC, ventromedial prefrontal cortex; PPTN, pedunculopontine nucleus; VTA, ventral tegmental area; NAcc, nucleus accumbens; VP, ventral pallidum; LHb, lateral habenula; RMTg, rostromedial tegmental nucleus.