Figure 2.
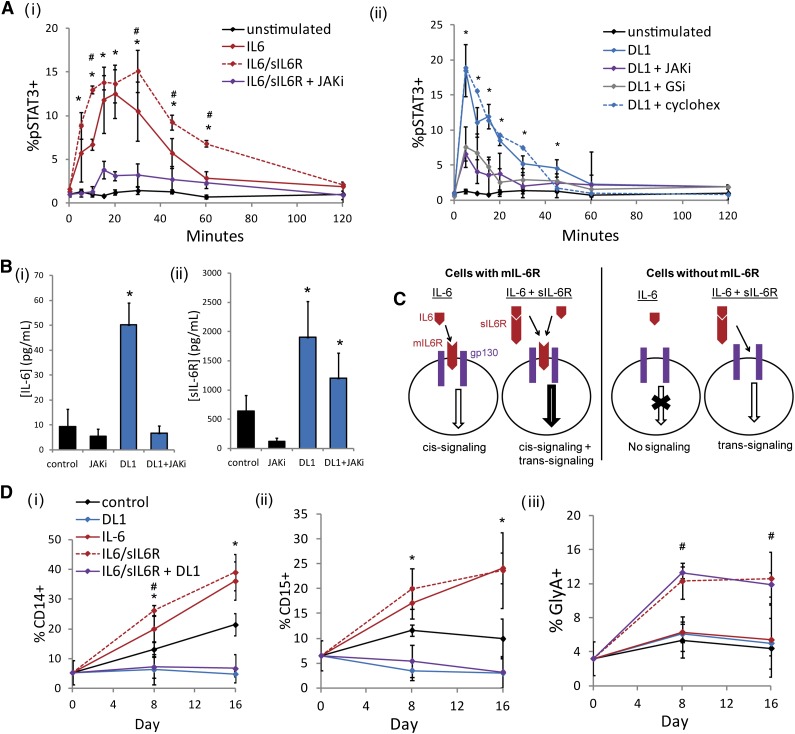
DL1 activates STAT3 similarly to IL-6 but impacts mature cells differently. (Ai) IL-6 stimulation activated STAT3 on cultured CD34+ cells. This effect was enhanced with the combination of IL-6 and sIL-6R and diminished by the addition of a JAKi. *Statistical comparison of IL-6 stimulation to unstimulated condition; #statistical comparison of IL-6/sIL-6R stimulation to IL-6 stimulation. (Aii) DL1 stimulation activated STAT3 on cultured CD34+ cells and was dependent on both JAK and γ-secretase (GSi) but was not impacted by cycloheximide. (B) DL1 upregulated the secretion of (i) IL-6 and (ii) sIL-6R. (C) Schematic of IL-6 cis-signaling and trans-signaling. IL-6 ligand can initiate JAK-STAT signaling in the absence or presence of sIL-6R on cell types that express mIL-6R (cis-signaling). On cells that do not express mIL-6R, IL-6–mediated signaling can occur only in the presence of sIL-6R (trans-signaling). (D) IL-6 increased CD14+ cells and CD15+ cells. The addition of sIL-6R additionally increased GlyA+ cells. The combination of IL-6/sIL-6R and DL1 inhibited the production of (i) CD14+ cells and (ii) CD15+ cells and maintained the production of (iii) GlyA+ cells. *Statistical comparison of IL-6 to control condition; #statistical comparison of IL-6/sIL-6R to IL-6 condition. All error bars indicate standard deviation. n ≥ 3, P < .05.