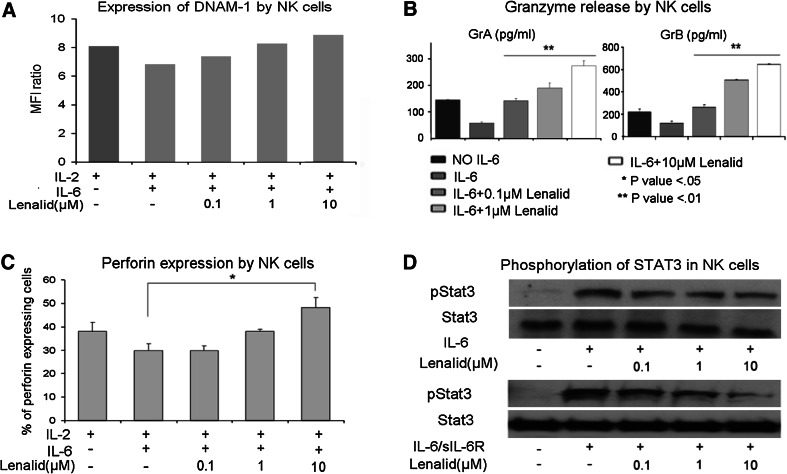
Fig. 4.
Suppression of NK cell cytotoxicity-related functions and activation of STAT3 by IL-6 is prevented by lenalidomide. a Purified NK cells (5 × 105 cells/ml) were cultured for 72 h with IL-2 alone (10 ng/ml) or with addition of IL-6 (10 ng/ml) and lenalidomide as indicated, and then the expression of DNAM-1 was evaluated with flow cytometry. A similar pattern of little or no effect was observed for NKG2D, NKp46, CD16, CD56, and CD107a (data not shown). b NK cells (5 × 105 cells/ml) were cultured for 72 h with IL-2 alone (10 ng/ml) or with added IL-6 (10 ng/ml) and lenalidomide as indicated, and then granzymes A and B were quantified in the CM with the CBA assay (mean ± SD for 3 replicate cultures for each condition). Confirmatory results were obtained with 2 additional experiments. c NK cells (5 × 105 cells/ml) were cultured for 72 h with IL-2 alone (10 ng/ml) or with added IL-6 (10 ng/ml) and lenalidomide, and then intracellular perforin was analyzed by flow cytometry. The percent of NK cells expressing perforin in the different culture conditions is shown (mean ± SD for 3 replicate cultures for each condition). Confirmatory results were obtained with 2 additional experiments. d NK cells were preincubated (20 min) with lenalidomide at the indicated concentrations, treated with IL-6 (10 ng/ml) or IL-6 plus sIL-6R (25 ng/ml) for 30 min, and then lysed for the analysis of phosphorylated STAT3 by Western blotting. Densitometry confirmed that lenalidomide inhibited phosphorylation of STAT3. Confirmatory results were obtained with 1 additional experiment. The t test P values *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01