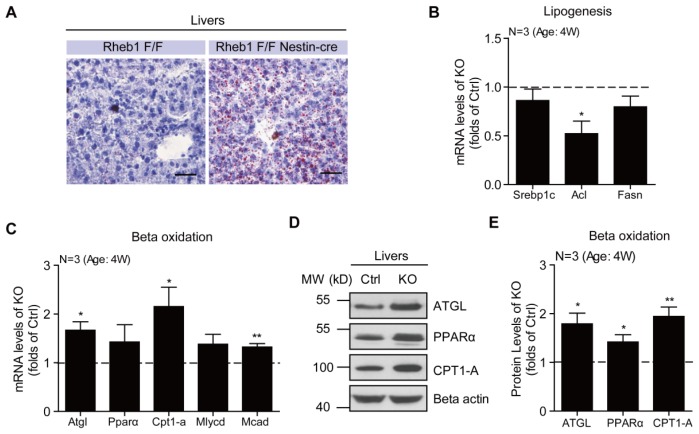
Figure 4.
Genetic deletion of Rheb1 in the brain increases liver lipid droplets and beta oxidation. (A) Representative oil red O staining images showing increased number of lipid droplets in livers of Rheb1 ko mice. Bar 25 μm; (B) Real-time PCR assays showing that hepatic lipogenesis genes Srebp1c, Acl and Fasn are not increased in livers of Rheb1 ko mice (N = 3). Results are averages of three independent animals. Data represent mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05; (C) Real-time PCR assays showing the increasing of mRNA levels of beta-oxidation genes, Atgl, Pparα, Cpt1-a, Mlycd and Mcad in livers of Rheb1 ko mice (N = 3). Results are averages of three independent animals. Data represent mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01; (D,E) Western blots and histograms showing the increasing of protein levels of ATGL, PPARα and CPT1-A in livers of Rheb1 ko mice (N = 3). Results are averages of three independent animals. Data represent mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.