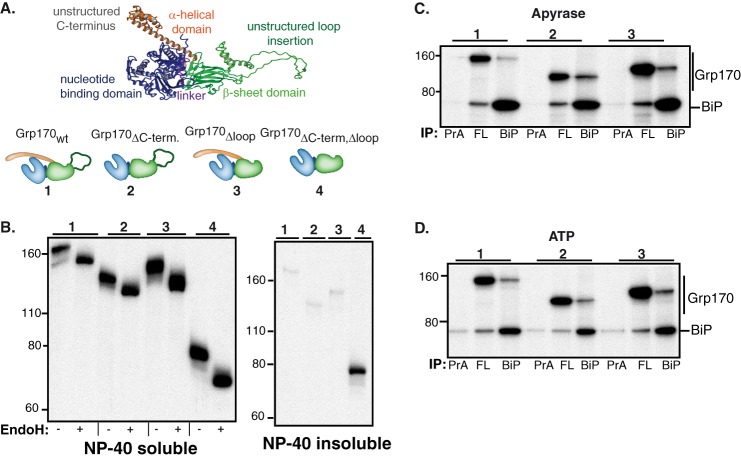
FIGURE 5.
Construction and characterization of Grp170 domain deletion mutants. A, schematic of the structural organization of Grp170 and the domain deletion mutants (blue: NBD, magenta: linker, green: β-sheet domain and unstructured loop insertion, orange: α-helical domain). The structure of human Grp170 (shown in ribbon) was modeled using Yasara Structure (www.yasara.org) based on the crystal structures of its cytosolic yeast orthologue Sse1p (13, 14, 40) and used to design FLAG-tagged Grp170 whole domain deletion mutants, which are numbered. B, COS-1 cells were transfected with empty pSVL vector, BiP, and the indicated Grp170 constructs. After a 1 h pulse-label with [35S]cysteine/methionine and a 1 h chase, cells were lysed in the presence of ATP. After centrifugation, samples were divided into Nonidet P-40 soluble and Nonidet P-40 insoluble fraction and immunoprecipitated with antiserum against the FLAG-tag. The eluted protein from cell lysates was divided and left undigested or treated with Endo H. Samples were analyzed by 10% SDS-PAGE, followed by autoradiography. The numbers above each group correspond to the deletion mutants shown in A. C and D, COS-1 cells were transfected with BiP and the indicated Grp170 constructs. After labeling with [35S]cysteine/methionine for 5 h and a chase period of 16 h, cells were lysed in the presence of apyrase (C) or ATP (D). Cell lysates were divided equally and immunoprecipitated with an antiserum against either the FLAG-tag (FL), BiP, or protein A (PrA) only. The proteins were separated on 10% SDS-PAGE, followed by autoradiography. Deletion mutants are indicated by the number above each group.