FIGURE 5.
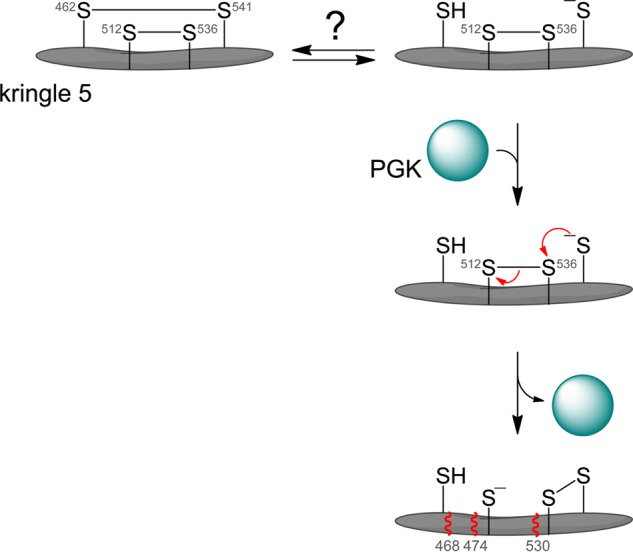
Model for the mechanism of angiostatin formation from plasmin(ogen). The Cys462-Cys541 disulfide bond is reduced in a fraction of plasminogen in blood or in the injured vascular wall. We propose that binding of PGK to plasmin induces a conformational change in kringle 5 that leads to attack by the Cys541 thiolate anion (present as a certain percentage of all thiols by action of the buffer) on the Cys536 sulfur atom of the Cys512-Cys536 disulfide bond, resulting in reduction of the bond. Cleavage of the disulfide allows further conformational change and exposure of the peptide backbone to proteolysis C-terminal of residues 468, 474, and 530 (represented by wavy red lines).
