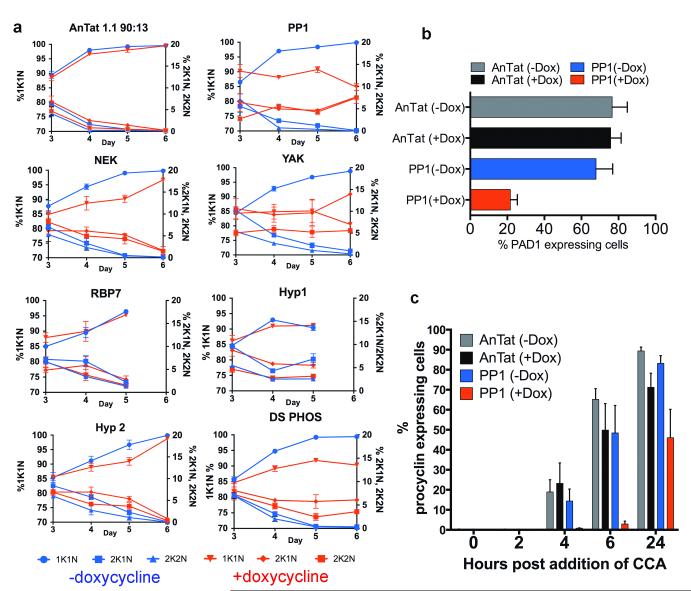
Figure 3. Silencing the identified genes reduces G1 arrest and differentiation competence.
a. Cell-cycle status of pleomorphic RNAi lines. n=6; mean ±s.e.m. percentage 1 kinetoplast (K), 1 nucleus (N) (G0/G1, plus S-phase cells; left Y-axis), 2K1N (G2-phase cells) or 2K2N (post-mitotic cells) (both right Y-axis) are shown. Test genes showed a signficant difference (GLMM, p<0.001) in comparison to AnTat1.1 90:13 +doxycycline on at least one day of infection.
b. PAD1 expression on day 6 post-infection (n=3/group, mean ±s.e.m.). PP1 RNAi cells show reduced PAD1 expression (GLM, F1,4=22.35, p=0.009).
c. PP1-depleted cells show signficantly reduced Procyclin expression during differentiation (GLM, F1,4=10.87, p=0.030) Bars represents mean ±s.e.m; n=3.