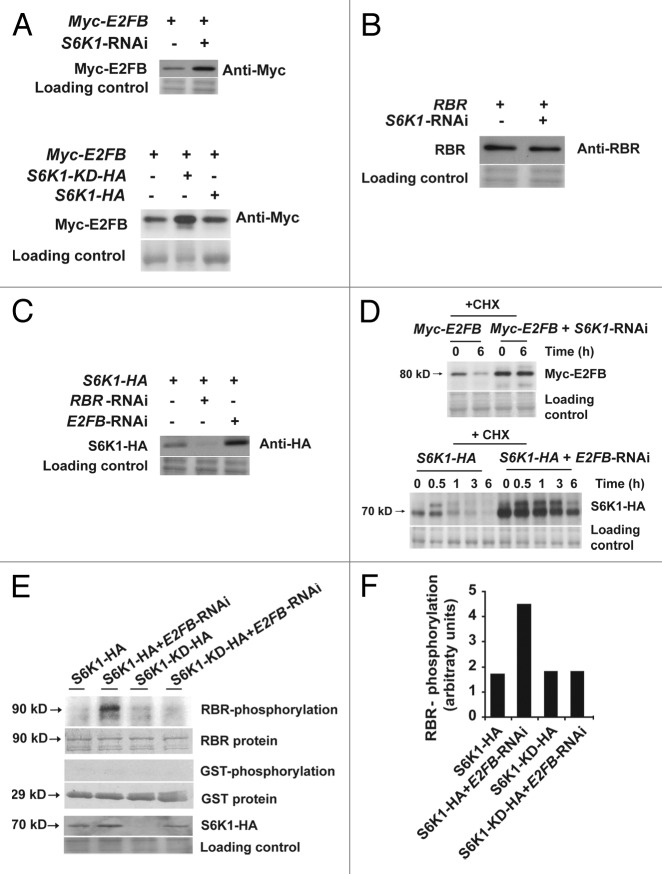
Figure 2. Mutual inhibition of S6K1 and E2FB is regulated at the stability and activity levels. (A) S6K regulates E2FB accumulation. Detection of Myc-E2FB expressed from a construct transformed to control cells (first lane, upper panel) or to cells co-transformed with the S6K1-RNAi (second lane, upper panel). Myc-E2FB in control cells (first lane, lower panel), in cells co-transformed with S6K1-KD-HA, a kinase-dead form with the active center mutated (second lane, lower panel) and in cells co-transformed with S6K1-HA (third lane, lower panel). (B) RBR expressed from a construct transformed to control cells (first lane) or in cells co-transformed with the S6K1-RNAi construct (second lane). (C) RBR-E2FB regulate S6K1 accumulation. S6K1-HA expressed from a construct transformed to control cells (first lane), to cells co-transformed with the RBR-RNAi (second lane) or to cells co-transformed with E2FB-RNAi (third lane). (D) Regulation of E2FB and S6K stability. Upper panel: detection of Myc-E2FB expressed from a construct transformed to control cells or to cells co-transformed with the S6K1-RNAi construct in the presence of 100 μM of cycloheximide (CHX) at 0 and 6h. Lower panel: detection of S6K1-HA expressed from a construct transformed to control cells or to cells co-transformed with the E2FB-RNAi construct in the presence of 100 μM of CHX from 0 to 6h. (E) Phosphorylation of RBR-pocket-GST fusion protein (first row) and only GST (third row) with immunopurified S6K1-HA and S6K1-KD-HA expressed in control cells or in cells where E2FB was silenced by RNAi (E2FB-RNAi). Fifth row: detection of S6K1-HA in these samples. Note the elevated expression level of S6K1-HA when E2FB was silenced, a result that corresponds to (A). (F) Quantification of the phosphorylation signals shown in (D).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.