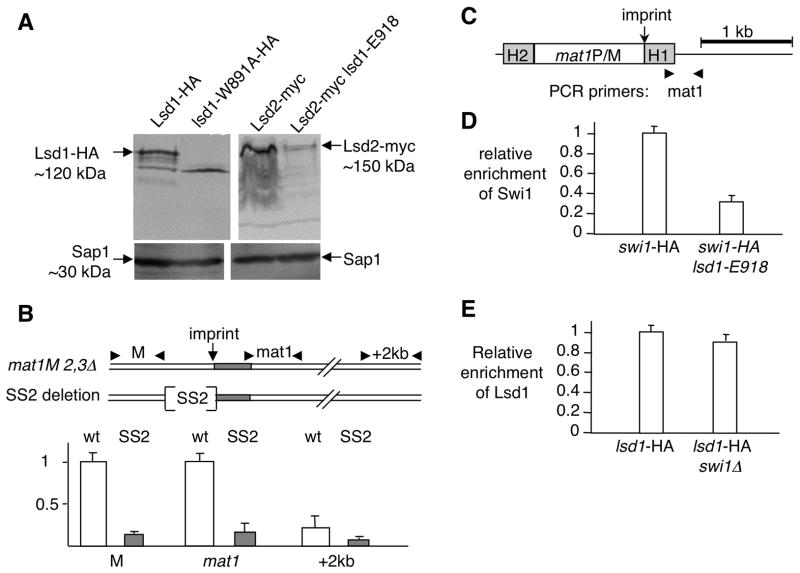
Figure 4. Lsd1 functions at mat1 to promote replication fork pausing at MPS1.
(A) The HMG domain of Lsd1 stabilizes the Lsd1/2 complex. Western blot of Lsd1-HA and Lsd2-myc tagged proteins in wt and HMG mutant strains. Sap1 protein is used as a loading control.
(B) Lsd1 binds to the SS2 cis-acting element proximal to the imprint site at mat1. Schematic representation of the wild type (wt) and deletion (SS2: 110 bp) region and primers used for the ChIP experiment. The two sets of primers are localized ~200 bp to the left (M) and ~100 bp to the right of the imprint (mat1). Quantitative PCR analysis of the ChIP for both wt lsd1-myc and SS2 lsd1-myc strains are shown.
(C) Schematic representation of the mat1 region and primers used for the ChIP experiment. The PCR primer pair (mat1) overlaps the imprinting regulatory region from mat1.
(D) Lsd1 recruitment is Swi1-independent. Quantitative PCR analysis of the ChIP of Lsd1-HA in the swi1+ and swi1 Δ backgrounds. Lsd1- HA swi1+ was set to 1.
(E) Swi1 recruitment is Lsd1-dependent. Quantitative PCR analysis of the ChIP of Swi-HA in the lsd1+ and lsd1-E918 backgrounds. Swi1-HA lsd1+ was set to 1.