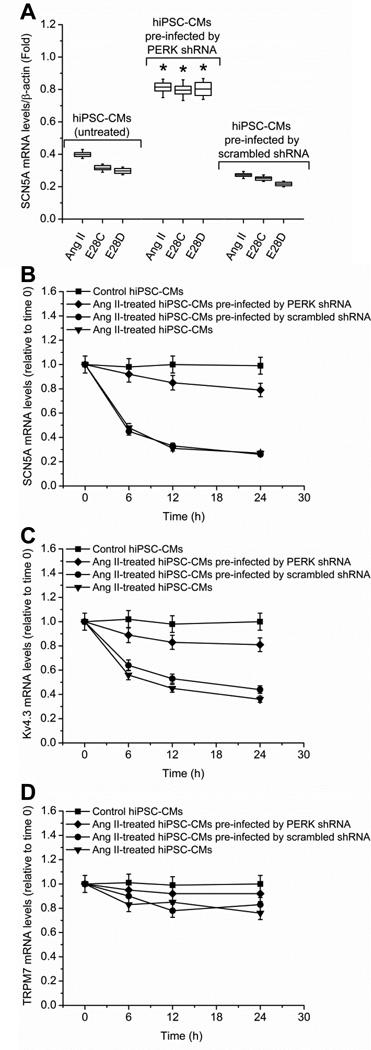
Figure 3.
PERK is involved in the SCN5A variant-mediated downregulation of full-length SCN5A. (A) Hypoxia, AngII (200 nmol/L), or overexpression of variant E28C or E28D constructs reduced full-length SCN5A mRNA. In each case, this reduction was inhibited by anti-PERK shRNAmir. Pre-infection by scrambled shRNA had no effect on the SCN5A mRNA reduction by any treatment. qPCR measurements by three duplicates are shown at 24 h in each treatment group and normalized by β-actin (* P < 0.05 compared with control group, n = 5 for each experimental group). PERK-mediated mRNA decay assays for SCN5A, Kv4.3 and TRPM7 are shown in panels B-D, respectively. Control (closed squares), AngII-treated (200 nmol/L, inverted triangles), AngII-treated with pre-infection by anti-PERK shRNAmir (closed diamonds), and AngII-treated with pre-infection by scrambled shRNA (closed circles) groups are shown. mRNA was harvested for each group at 0, 6 h, 12 h, and 24 h. The target genes were measured by qPCR and normalized to β-actin. The error bars in panels B-D represented standard error (SE). AngII treatment reduced SCN5A (P = 0.019, n = 5 for each experimental group) (B) and Kv4.3 (P = 0.042, n = 5 for each experimental group) (C) mRNA stability when compared to control while having no effect on TRPM7 (P = 0.078, n = 5 for each experimental group) (D). Pre-infection by pGIPZ lentiviral anti-PERK shRNAmir but not scrambled shRNA could prevent mRNA instability (P = 0.027, n = 5 for each experimental group).