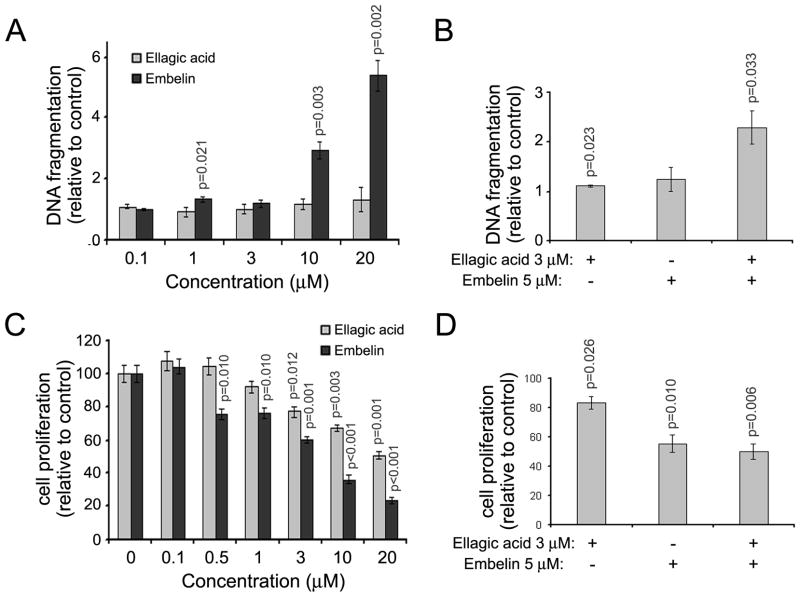
Figure 5. Ellagic acid and embelin induce apoptosis and decrease proliferation in cultured mouse pancreatic stellate cells.
Culture-activated mouse pancreatic stellate cells were incubated for 72 h in 1% FBS-containing medium in the presence or absence of embelin and/or ellagic acid. (A and B) Apoptosis was assessed by measuring DNA fragmentation (Roche ELISA). (C and D) Cell proliferation was estimated by MTT assay. Graphs showed mean ± SEM of 3–4 independent studies. P-values are for one-sided one-sample t-tests comparing with controls (1 for A and B, 100 for C and D). For A and C, the effects of ellagic acid and embelin were tested separately. For B and D, the synergistic effects (defined similar to Fig. 3) were tested. With Bonferroni’s adjustment, p<0.01 is considered as significant in A, p<0.0071 are considered significant in C, and p<0.0125 are considered significant in B and D. P-values greater than 0.05 are indicated in the figures. At the indicated doses, Ellagic acid and embelin had a synergistic effect on apoptosis (5B; p=0.033) but not on cell proliferation (5D; p=0.999).