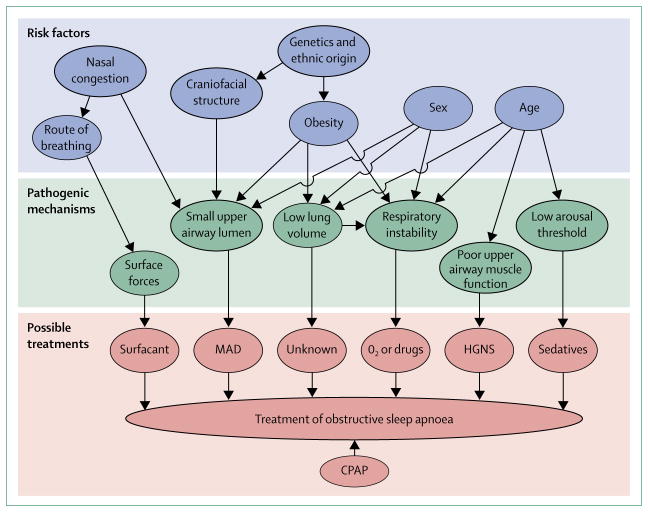
Figure 3. Risk factors, pathogenic mechanisms, and possible treatments for obstructive sleep apnoea.
Risk factors for obstructive sleep apnoea probably act through one or more pathogenic mechanisms. One or two of the pathogenic mechanism might predominate in each patient and give rise to the disorder. Although CPAP treats obstructive sleep apnoea irrespective of underlying cause, treatments based on tackling individual pathogenic mechanisms might prove a successful alternative approach—eg, fluid accumulation outside the airway could make the upper airway lumen smaller and might respond to diuretic treatment. CPAP=continuous positive airway pressure. MAD=mandibular advancement device. HGNS=hypoglossal nerve stimulation.