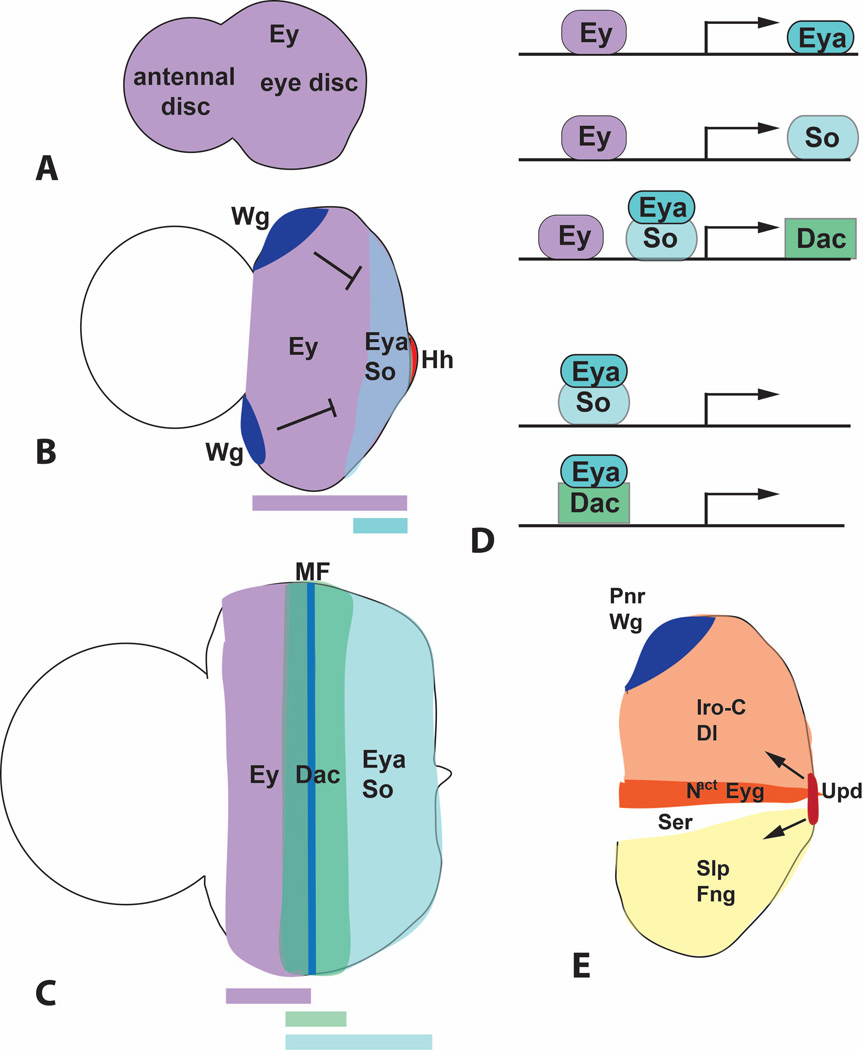
Figure 3. Retinal determination genes.
(A–C) are diagrams showing the expression pattern of Ey, Eya, So and Dac in first instar (A), second instar (B) and third instar (C) eye-antennal discs. Colored bars below the diagrams indicate the regions in which these expression domains overlap. Repression of eya by anterior Wg and its activation by posterior Hh is indicated in (B). MF, morphogenetic furrow. (D) represents the functional relationships between these transcription factors. Ey directly activates eya and so transcription, and Ey, Eya and So all contribute to dac activation. Eya can interact with the DNA-binding protein So to form a compound transcription factor that regulates downstream genes, and may also regulate gene expression in a complex with Dac. (E) shows the expression domains of some of the factors that drive dorsal-ventral compartmentalization and growth of the early eye disc. Dorsally expressed Pnr activates wg expression, and Wg then establishes the expression domains of the Iro-C and Slp transcription factors. These control the compartmentalized distribution of Notch ligands and modifying enzymes that lead to Notch activation at the dorsoventral midline. Downstream targets of Notch that regulate growth include the transcription factor Eyg and the long-range signaling molecule Upd.