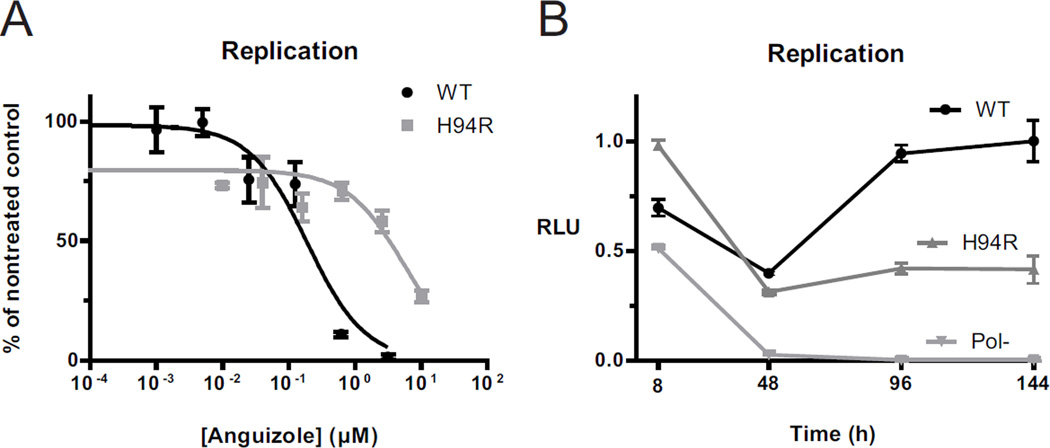
Figure 3.
Characterization of the H94R resistance mutation. (A and B) Transient luciferase replication assays were performed with genotype 1b HCV replicon constructs containing either a histidine (WT, black) or an arginine (H94R, dark gray) at amino acid 94 in the NS4B sequence. (A) Luciferase assays were performed following 5 days of treatment with various concentrations of anguizole. Replication levels (RLU) are shown relative to the maximal luminescence observed for each electroporation, and they are normalized to cell viability measurements for each sample. EC50 values were calculated to be 0.20 µM for WT and 7.5 µM for the H94R mutant. (B) Replication kinetics were tested for these constructs, along with a polymerase defective control (Pol-, light gray), over a 6-day period in the absence of anguizole. Replication levels are shown relative to the maximal luminescence observed for all electroporations. Compared to wild-type, the H94R mutant is impaired in its replication ability. Each data point is the mean of three replicates and error bars represent SEM.