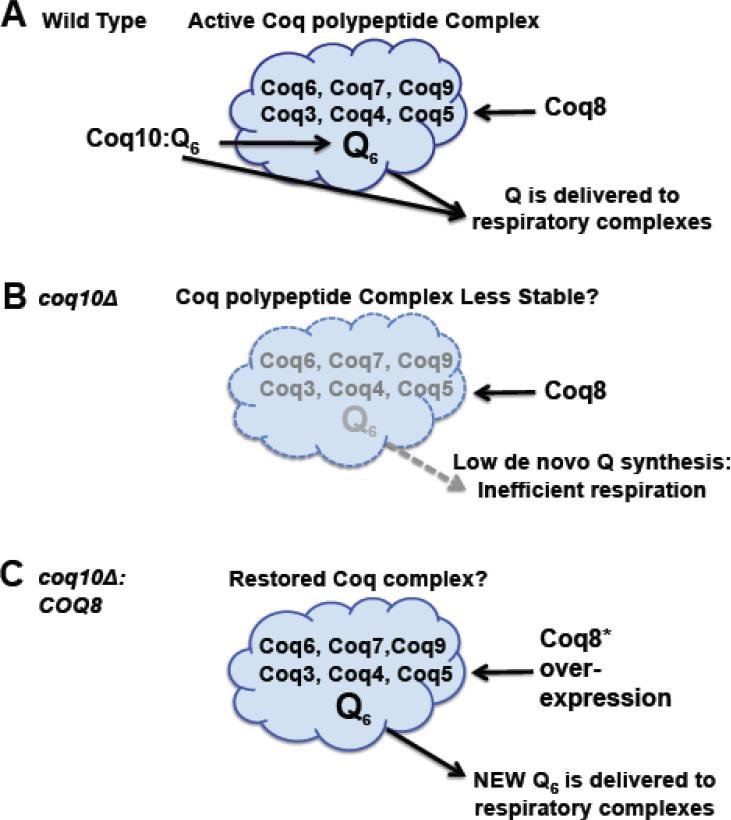
Figure 11.
A model for Coq10/START domain polypeptide function in de novo Q6 biosynthesis and in delivery of Q6 to respiratory chain complexes. (A) In wild-type cells, the Coq10:Q protein:ligand complex is postulated to deliver Q6 to the multisubunit Coq polypeptide complex and so enhance stability of the Coq polypeptides and de novo synthesis of Q6. Newly synthesized Q6 in the mitochondrial inner membrane is delivered to respiratory chain complexes and can function as an antioxidant. We postulate that Coq10:Q6 may also deliver Q6 to respiratory complexes. (B) The coq10 null mutant contains lower steady state levels of Coq polypeptides [20] and is shown with a less stable multisubunit Coq complex. Impaired de novo synthesis of Q6 and lack of Coq10:Q6 delivery to respiratory complexes accounts for the inefficient respiration observed in the coq10 null mutant. (C) The coq10 null mutant can be rescued by over-expression of COQ8, via its ability to restore the Coq polypeptide complex [25]. We postulate that the enhanced de novo Q6 biosynthesis formed by the Coq multisubunit complex is efficiently delivered to respiratory complexes, despite the absence of Coq10p.