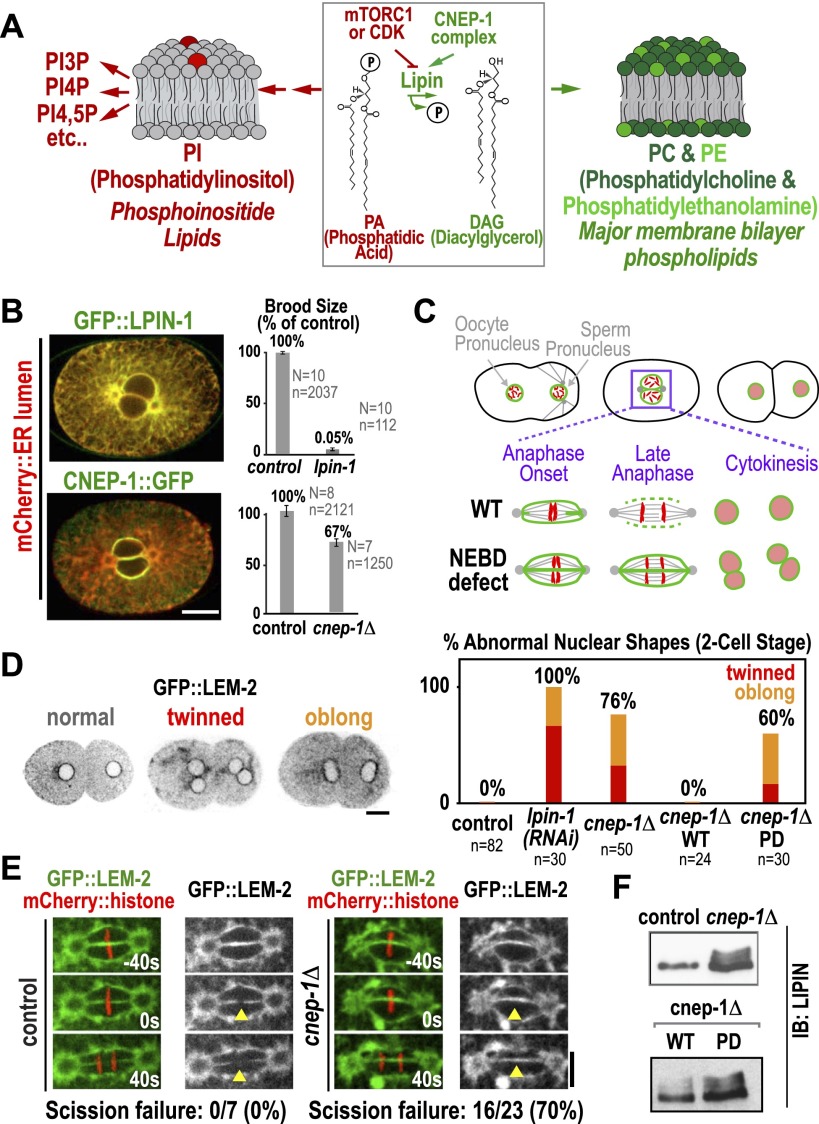
Figure 1.
The lipin activator CNEP-1 concentrates on the nuclear envelope and is required for timely nuclear envelope disassembly during mitosis. (A) Schematic showing lipin at the branching point between the synthesis of major membrane phospholipids and PI. (B) Fluorescence confocal images of embryos expressing the ER lumen marker mCherry∷SP12 along with GFP∷LPIN-1 (top) (n > 10 embryos) or mCherry∷SP12 and CNEP-1∷GFP in a background deleted for the endogenous cnep-1 gene (bottom) (n > 10 embryos). Graphs plot normalized brood size. Error bars are SEM. (N) Number of worms; (n) total number of embryos. (C) Schematics highlight scission of the maternal and paternal pronuclear envelopes (green) during chromosome (red) segregation in the first division of control C. elegans embryos and failure of scission in embryos exhibiting a nuclear envelope breakdown (NEBD) defect. (D, left) Inverted contrast fluorescence confocal images of two-cell stage embryos expressing GFP∷LEM-2 illustrate nuclear morphology phenotypes. (Right) Graph plotting frequency of abnormal nuclear phenotypes for the indicated conditions. (E) Fluorescence confocal images of control and cnep-1Δ embryos expressing GFP∷LEM-2 and mCherry∷histone. Times are in seconds relative to anaphase onset. Yellow arrowheads mark the site of nuclear envelope scission in wild type. (F) Immunoblots of lysates from control and cnep-1Δ worms (top) or cnep-1Δ worms harboring the wild-type (WT) or PD transgenes (bottom) probed for LPIN-1. Bars, 10 μm.