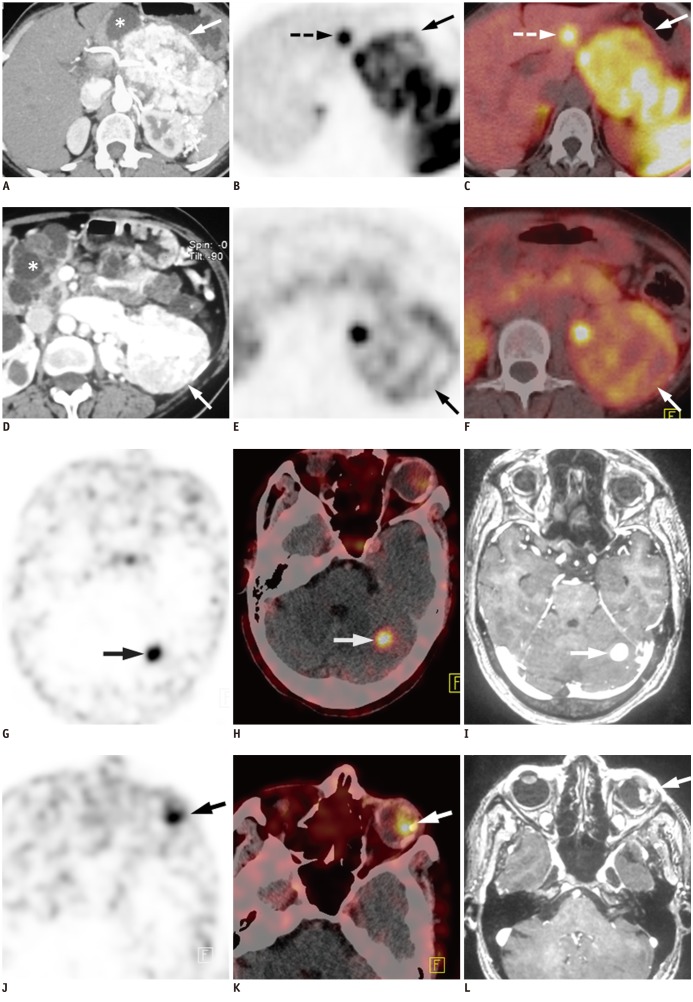
Fig. 1.
52-year-old female with Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome.
Transaxial contrast enhanced CT (A) of abdomen show large (9.6 × 7.4 × 5.4 cm) mass lesion in region of body and tail of pancreas with intense post contrast enhancement (arrow). Multiple cysts of varying sizes are noted in rest of pancreas (asterix). Also, note tortuous blood vessels in peripancreatic and perisplenic location. Transaxial PET (B) and PET-CT (C) images show intense heterogeneous uptake of 68Ga-labelled [1, 4, 7, 10-tetraazacyclododecane-1, 4, 7, 10-tetraacetic acid]-1-Nal3-Octreotide (68Ga-DOTANOC) (SUVmax = 18.6) in pancreatic mass (arrow), thus confirming it to be NET. Focal 68Ga-DOTANOC uptake (SUVmax = 13.2) was also seen in segment III of liver (B, C, broken arrow) suggesting liver metastasis from pancreatic NET. This was confirmed at fine needle aspiration cytology. Transaxial contrast enhanced CT (D) of abdomen also shows another mass (7.8 × 5.8 × 5.1 cm) arising from interpolar region of left kidney and showing intense post contrast enhancement (arrow). Multiple feeding vessels are seen to arise from left renal artery and supply mass. These findings were suggestive of RCC. Also noted are bilateral multiple renal cortical cysts (asterix). PET (E) and PET-CT (F) images reveal mild 68Ga-DOTANOC uptake (SUVmax = 3.1) in renal mass (arrow). Transaxial PET (G) and PET-CT (H) images of brain show focal area of 68Ga-DOTANOC uptake (SUVmax = 9.9) in hypodense lesion (2 × 2 cm) in left cerebellum (arrow). Transaxial T2 weighted gadolinium enhanced MRI (I) of brain reveals nodular lesion in lateral half of left cerebellar hemisphere with intense post contrast enhancement (arrow), suggesting hemangioblastoma. Transaxial PET (J) and PET-CT (K) images also revealed focal 68Ga-DOTANOC uptake (SUVmax = 8.3) in lateral part of left globe, corresponding to heterogeneous nodular lesion (arrow). Transaxial T2 weighted gadolinium enhanced MRI (L) showed eccentric nodule in lateral part of left globe with intense post contrast enhancement, suggesting retinal hemangioblastoma (arrow).