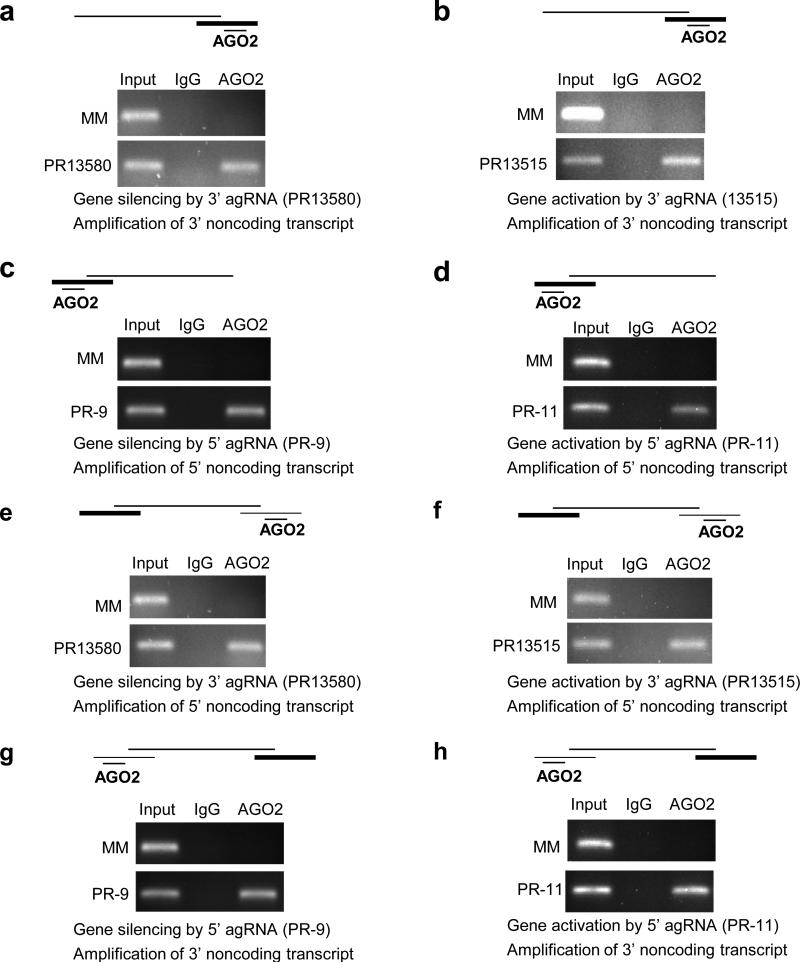
Figure 6. Effect of 3’ or 5’ agRNAs on recruitment of AGO2 protein to the 3’ or 5’ noncoding transcripts at the PR locus.
RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) of 3’ noncoding RNA using an anti-AGO2 antibody after treatment with (a) inhibitory RNA PR13580 in T47D cells or (b) activating RNA PR13515 in MCF7 cells on recruitment of AGO2 protein to the 3’ noncoding transcript. Effect of adding (c) inhibitory RNA PR-9 to T47D cells or (d) activating RNA PR-11 to MCF7 cells on recruitment of AGO2 protein to the 5’ noncoding transcript. Effect of adding (e) inhibitory RNA PR13580 to T47D cells or (f) activating RNA PR13515 to MCF7 cells on co-immunoprecipitation of AGO2 protein with the 5’ noncoding transcript. Effect of adding (g) inhibitory RNA PR-9 to T47D cells or (h) activating RNA PR-11 to MCF7 cells on co-immunoprecipitation of AGO2 protein with the 3’ noncoding transcript. The scheme above each gel depicts PR mRNA, the 3’ and/or 5’ noncoding transcripts, and AGO2 bound agRNA. The heaviest line represents the transcript being amplified. Duplex RNAs were added to cells at 25 nM. Experiments are representative of two independent determinations.