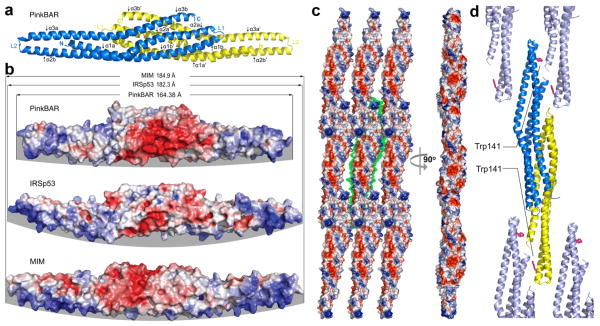
Figure 3.
Crystal structure and oligomerization of the BAR domain of Pinkbar. (a) Ribbon diagram representation of the structure of the BAR domain of Pinkbar. The two chains that form the BAR domain are colored yellow and blue. Each chain contains three α-helices, which are kinked toward their middle (see also Supplementary Fig. S6), and are thus labeled as α1a-α1b to α3a-α3b (or α1a′-α1b′ to α3a′-α3b′ for the second chain). (b) Electrostatic surface representation of the BAR domain of Pinkbar compared to those of IRSp53 and MIM. Blue and red indicate negatively and positively charged regions, respectively. Note that the BAR domain of Pinkbar is shorter and its membrane-binding surface (highlighted by a gray background) less curved than those of IRSp53 and MIM. (c) The BAR domain of Pinkbar, which forms sheet-like membrane structures in solution, also forms a planar oligomer in the crystal lattice, in which the membrane-binding interface of individual BAR domains all face in the same direction (i.e. facing the reader in the view shown on the left). The green background highlights the boundaries of a single BAR domain dimer. This planar oligomer is somewhat reminiscent of the planar BAR-BAR coats observed by EM tomography of F-BAR domains 13. (d) The conspicuously exposed residue Trp141 may be involved in the stabilization of the lateral oligomer (the ribbon diagram is shown in a similar orientation as part c, left view), as suggested by light scattering analysis in solution of wild type and Trp141Ser mutant BAR domain constructs (see Supplementary Fig. 7a, b).