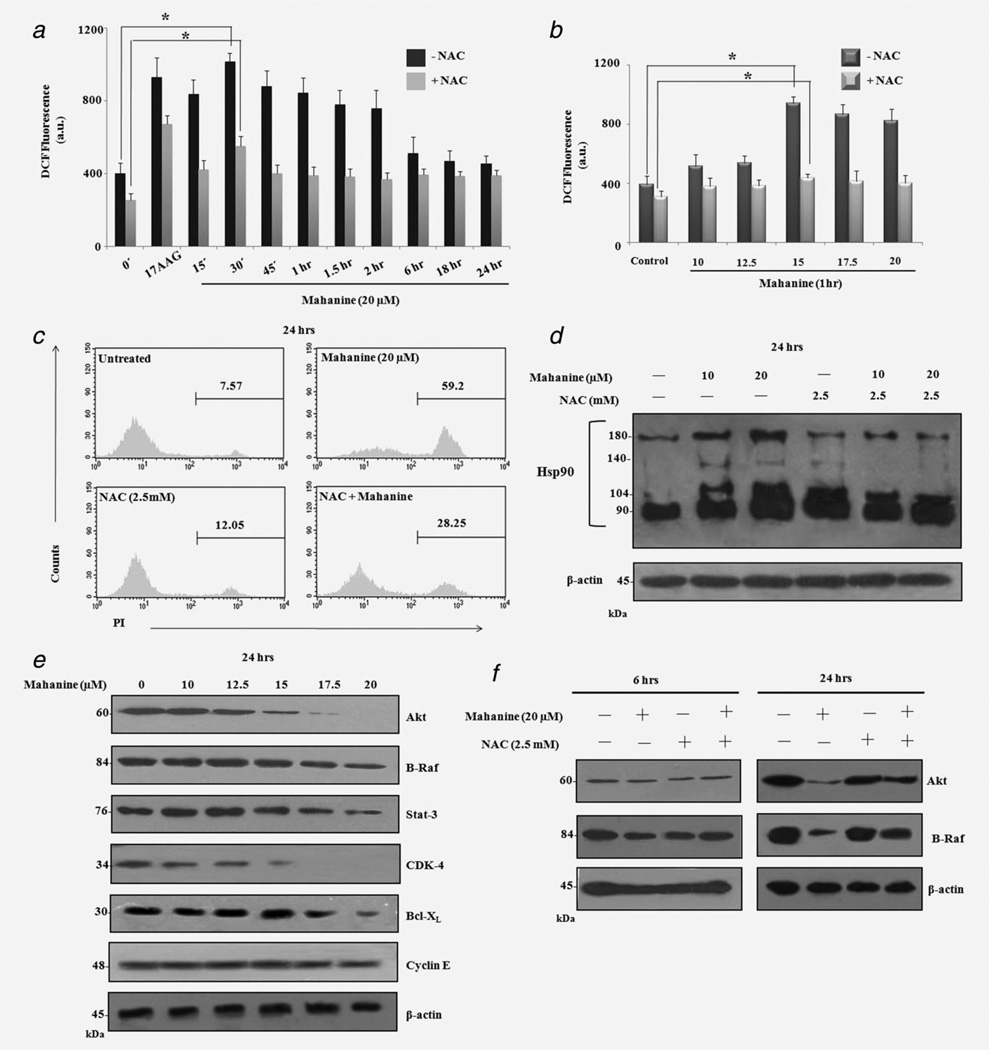
Figure 2.
Mahanine induces ROS accumulation in both a time- and dose-dependent manner, leading to Hsp90 dysfunction in MIAPaCa-2 cells. MIAPaCa-2 cells were subjected to 20 µM mahanine treatment for 0–24 hr. ROS production was measured by H2DCF-DA staining and was inhibited by 1 hr pretreatment of cells with NAC (2.5 mM). The17-AAG (1 µM) was used as a positive control. The results are expressed as MFI (a.u.) Each value is the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. “*” indicates p < 0.05. MIAPaCa-2 cells were subjected to mahanine (10–20 µM) treatment for 1 hr and processed as above. Each value is the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. “*” indicates a significant difference of p < 0.05. NAC (2.5 mM) treatment for 1 hr prevented the effect of 20 µM mahanine on cell viability, as reflected in the decrease of PI positivity by flow cytometric analysis after 24 hr. Mahanine-induced ROS-mediated Hsp90 dysfunction in MIAPaCa-2 cells. MIAPaCa-2 cells were treated with mahanine (10 and 20 µM) for 24 hr after preincubation without or with NAC (2.5 mM, for 1 hr). Experiments were performed as described in the Material and Methods section. Mahanine-induced ROS generation led to disulfide linkage of Hsp90, as shown by the slower migration rate on nonreducing SDS-PAGE, concentrated in higher molecular weight regions, which was ameliorated by subsequent NAC incubation. Mahanine downregulates the Hsp90 client proteins levels. MIAPaCa-2 cells were subjected to mahanine treatment for 24 hr and analyzed by Western Blot with the indicated antibodies. A dose-responsive decrease in the Hsp90 client protein levels in MIAPaCa-2 cells, whereas no down-regulation was observed in nonclient protein Cyclin E. ROS-dependent down regulation of Hsp90 client proteins. NAC-pre-treated (2.5 mM) MIAPaCa-2 cells were incubated with mahanine (20 µM) for 6 and 24 hr, respectively, and analyzed by Western Blot with the indicated antibodies. The presented data have been derived from three different experiments, one of which is shown here.