Abstract
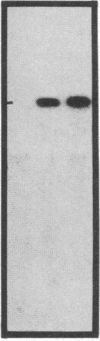
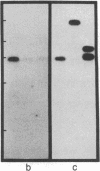
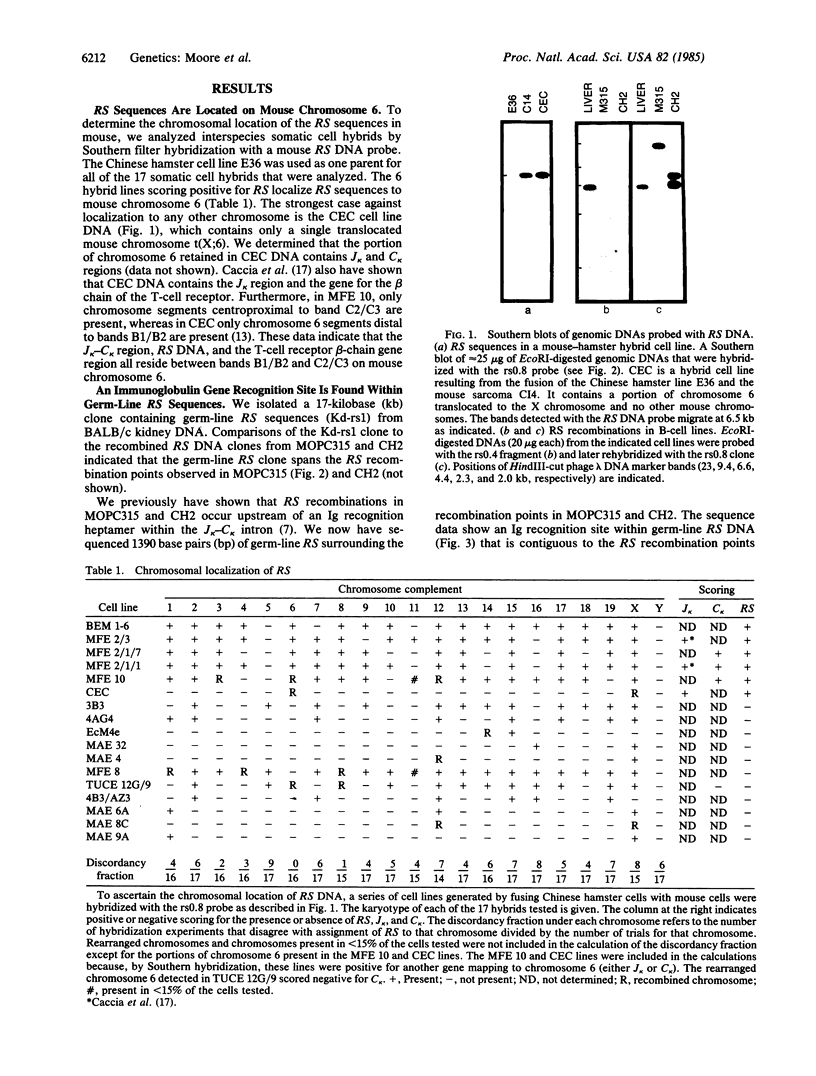
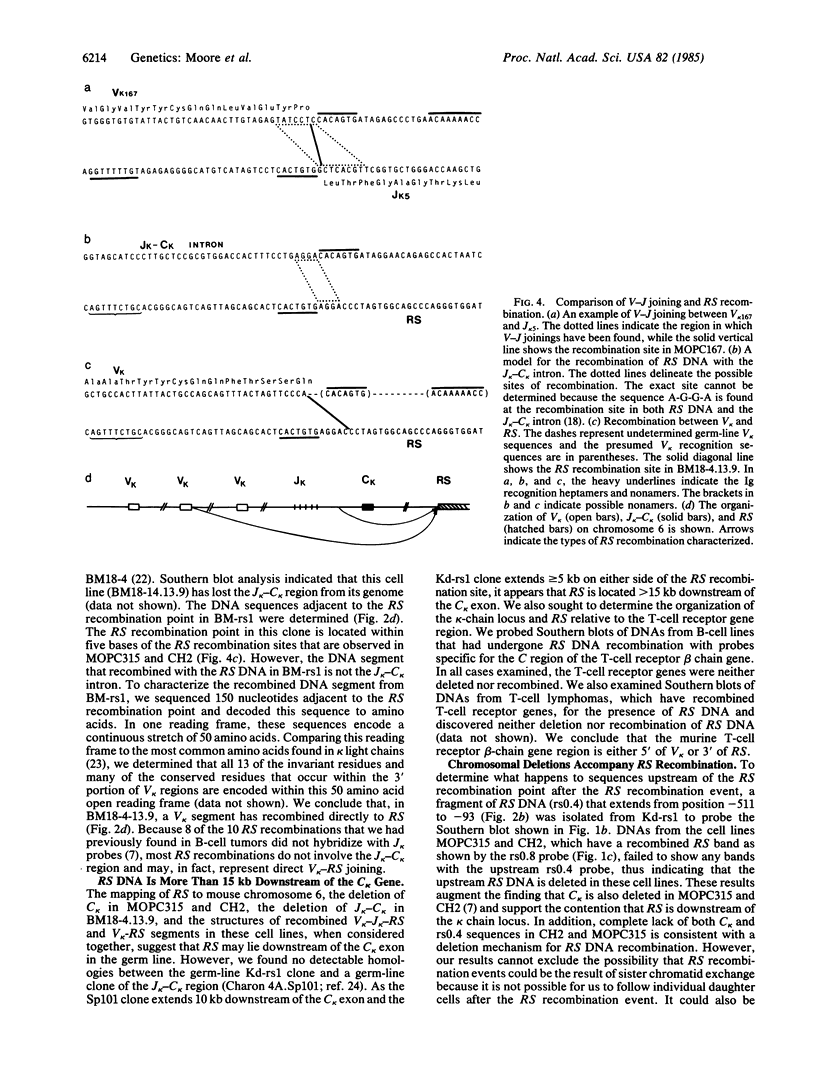
We isolated and characterized the germ-line counterpart of a DNA segment designated RS (for recombining sequence), that is frequently recombined in mouse lambda light chain-producing B lymphocytes. Using Southern blot analyses of myelomas and mouse-Chinese hamster fusion cell lines, we found that RS DNA sequences are located on mouse chromosome 6, evidently more than 15 kilobases downstream of the kappa light-chain locus. We find that a typical recognition site for Ig gene recombination is situated within germ-line RS sequences near the recombination points observed in at least two lambda chain-producing cell lines. This represents a complete and functional Ig recognition site that is not directly associated with Ig genes. We also characterized a recombined RS segment isolated from the cell line BM18-4.13.9. This recombined segment has a variable region kappa light chain gene (V kappa) joined directly to RS sequences. Our results suggest that the deletion of the kappa light chain constant region (C kappa) exon in many lambda chain-producing B cells is the result of RS recombination and that C kappa deletion may be mediated by the same processes as antibody gene V-J joining (J = joining segment gene). We discuss the potential biological significance of RS DNA recombination in B-cell maturation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Enea V., Bothwell A. L., Baltimore D. Activity of multiple light chain genes in murine myeloma cells producing a single, functional light chain. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caccia N., Kronenberg M., Saxe D., Haars R., Bruns G. A., Goverman J., Malissen M., Willard H., Yoshikai Y., Simon M. The T cell receptor beta chain genes are located on chromosome 6 in mice and chromosome 7 in humans. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1091–1099. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90443-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleclough C., Perry R. P., Karjalainen K., Weigert M. Aberrant rearrangements contribute significantly to the allelic exclusion of immunoglobulin gene expression. Nature. 1981 Apr 2;290(5805):372–378. doi: 10.1038/290372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durdik J., Moore M. W., Selsing E. Novel kappa light-chain gene rearrangements in mouse lambda light chain-producing B lymphocytes. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):749–752. doi: 10.1038/307749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Huang H., Davis M., Calame K., Hood L. An immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene is generated from three segments of DNA: VH, D and JH. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):981–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P. A., Korsmeyer S. J., Waldmann T. A., Leder P. Human immunoglobulin kappa light-chain genes are deleted or rearranged in lambda-producing B cells. Nature. 1981 Apr 2;290(5805):368–372. doi: 10.1038/290368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L., Cesareni G. Novel bacteriophage lambda cloning vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5172–5176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsmeyer S. J., Hieter P. A., Ravetch J. V., Poplack D. G., Waldmann T. A., Leder P. Developmental hierarchy of immunoglobulin gene rearrangements in human leukemic pre-B-cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7096–7100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S., Rosenberg N., Alt F., Baltimore D. Continuing kappa-gene rearrangement in a cell line transformed by Abelson murine leukemia virus. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):807–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Seidman J. G., Leder P. Sequences of five potential recombination sites encoded close to an immunoglobulin kappa constant region gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3450–3454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Hart C. P., Gehring W. J., Ruddle F. H. Molecular cloning and chromosome mapping of a mouse DNA sequence homologous to homeotic genes of Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):675–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90262-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., Bothwell A., Storb U. Physical linkage of the constant region genes for immunoglobulins lambda I and lambda III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3829–3833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patten P., Yokota T., Rothbard J., Chien Y., Arai K., Davis M. M. Structure, expression and divergence of T-cell receptor beta-chain variable regions. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):40–46. doi: 10.1038/312040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Hüppi K., Heinrich G., Tonegawa S. Sequences at the somatic recombination sites of immunoglobulin light-chain genes. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):288–294. doi: 10.1038/280288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Maki R., Kurosawa Y., Roeder W., Tonegawa S. Two types of somatic recombination are necessary for the generation of complete immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes. Nature. 1980 Aug 14;286(5774):676–683. doi: 10.1038/286676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsing E., Storb U. Somatic mutation of immunoglobulin light-chain variable-region genes. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):47–58. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90230-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):575–581. doi: 10.1038/302575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walfield A. M., Storb U., Selsing E., Zentgraf H. Comparison of different rearranged immunoglobulin kappa genes of a myeloma by electronmicroscopy and restriction mapping of cloned DNA: implications for "allelic exclusion". Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 24;8(20):4689–4707. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.20.4689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]