FIGURE 4:
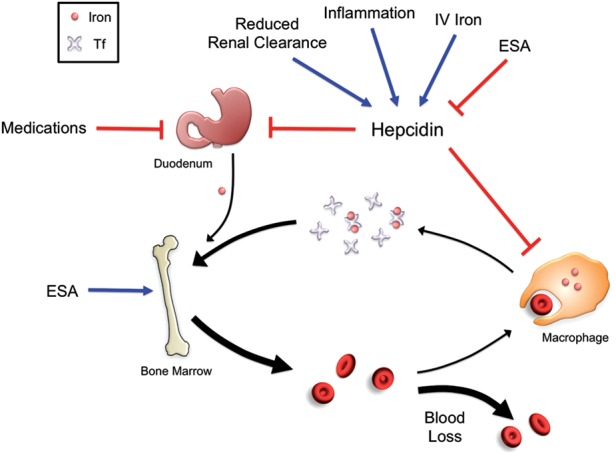
Disordered iron balance in CKD. Chronic inflammation and reduced renal clearance in patients with CKD lead to increased levels of hepcidin, which reduces duodenal iron uptake and iron release from cellular iron stores. Intestinal iron uptake is also inhibited by medications such as phosphate binders and antacids. ESAs stimulate increased iron usage for erythropoiesis, while blood loss due to frequent phlebotomy, blood trapping in the dialysis apparatus and gastrointestinal bleeding further deplete the circulating iron pool. Iron administration stimulates hepcidin expression, which can paradoxically worsen the iron restriction, while ESAs have an inhibitory effect on hepcidin expression.
