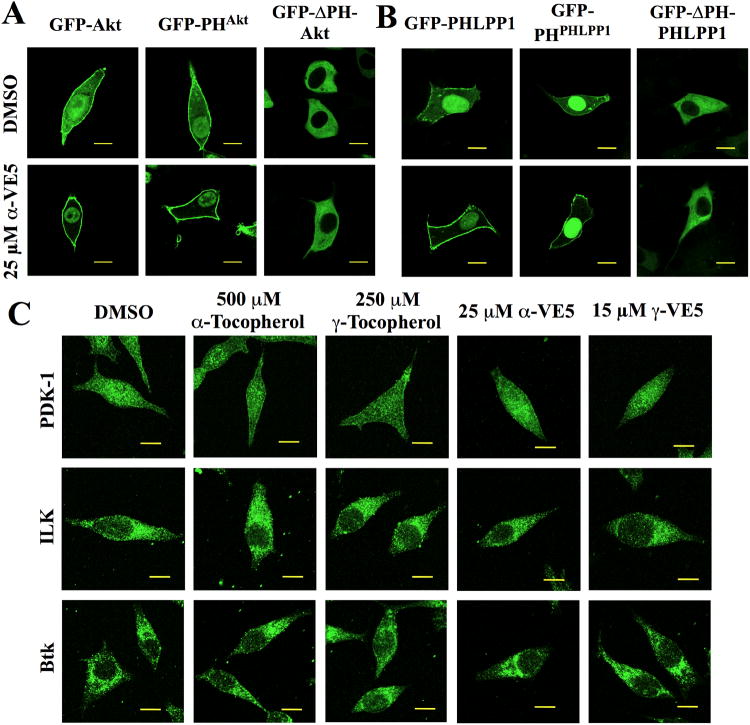
Fig. 6. Membrane recruitment of Akt and PHLPP1 by tocopherols and VE5 compounds is PH domain-dependent.
(A) Subcellular localization of green fluorescent protein (GFP)-tagged full length wild-type Akt (GFP-Akt), PH domain of Akt (GFP-PHAkt), and PH domain-deleted Akt (GFP-ΔPH-Akt) in LNCaP cells treated with α-VE5. Scale bars, 40 μm. Additional images from three independent experiments are shown in fig. S6A. (B) Subcellular localization of GFP-PHLPP1, GFP-PHPHLPP1, and GFP-ΔPHPHLPP1 in LNCaP cells treated as described in (A). Scale bars, 40 μm. Additional images from three independent experiments are shown in fig. S6B. (C) Subcellular distribution of PH domain-containing kinases PDK-1 (upper), ILK (middle), and BTK (lower) in LNCaP cells treated with tocopherols and VE5 compounds. Scale bars, 40 μm. Additional images from three independent experiments are shown in fig. S6C.