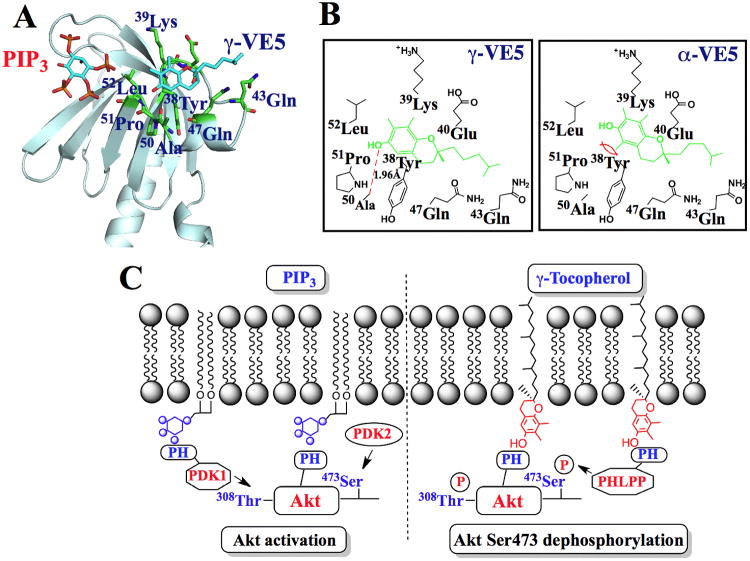
Fig. 7. Molecular modeling of the binding of α- and γ-VE5 with the Akt PH domain.
(A) A model for the docking of γ-VE5 into the VL2 loop of the PH domain of Akt. Binding of phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-triphosphate (PIP3) is also represented. (B) Modeled interactions of γ-VE5 (left) and α-VE5 (right) with amino acid residues of the VL2 domain of the Akt PH domain. VE5 compounds (green) and hydrogen bonding (red dashed line) are indicated. (C) Diagram depicting the mechanism of γ-tocopherol-mediated dephosphorylation of Akt at Ser473 in cancer cells (right) compared to that of PIP3-mediated Akt activation (left). PIP3, phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-triphosphate; PH, pleckstrin homology.