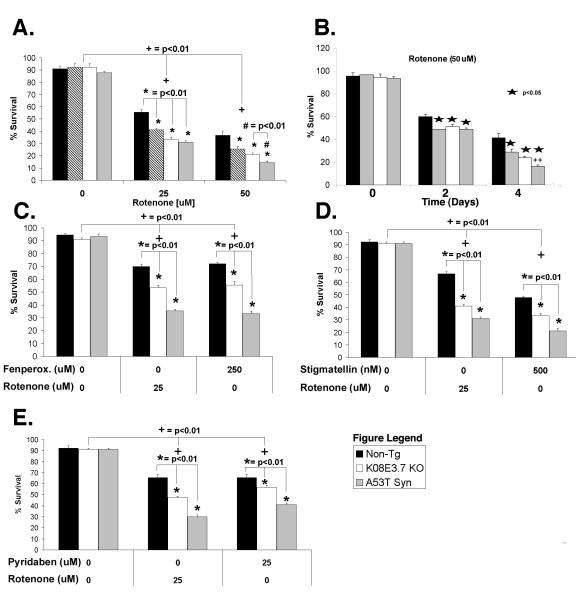
Figure 3. K08E3.7 KO, wild type and A53T α-synuclein expressing lines are selectively vulnerable to rotenone-induced toxicity.
(A & B.) K08E3.7 KO, wild type and A53T α-synuclein expressing lines show increased vulnerability to rotenone at varying doses (A; 25 or 50 μM rotenone, 4 days treatment), and at different times (B; 50 μM rotenone, 2 and 4 days treatment). The PD-related lines show enhanced vulnerability after 4 days of rotenone treatment; (*) p<0.01. At 50 μM rotenone, the A53T α-synuclein expressing strain is also more vulnerable than the wild type α-synuclein strain; (#) p<0.01. (+) p <0.01 compared to untreated of the same strain. (C – E) The K08E3.7 KO, wild type and A53T α-synuclein expressing strains show enhanced toxicity compared to the non-tg line after treatment for 4 days with complex I inhibitors fenperoximate (C), stigmatellin (D) and pyridaben (E), (*) p<0.01, (+) p<0.01 compared to untreated nematodes of the same line.