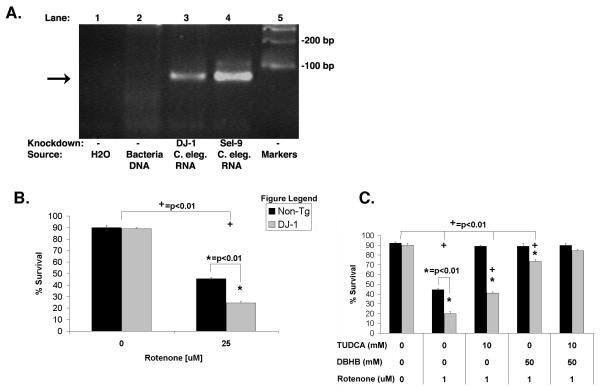
Figure 8. Knockdown of DJ-1 increases vulnerability to rotenone and is rescued by DβHB and TUDCA.
(A) Knockdown of DJ-1 increased the vulnerability to rotenone-induced toxicity. Lane 1: H2O alone, Lane 2: RNA from the bacteria containing the B0432.2 (DJ-1) fragment used for the knockdown, Lane 3: RNA from C. elegans used for B0432.2 (DJ-1) knockdown, Lane 4: RNA from C. elegans used for Sel-9 knockdown, Lane 5: DNA standards. Lane 2 did not produce an amplification product because the procedure for isolating RNA effectively removed the DNA plasmid used to generate the RNAi. (B) Knockdown of DJ-1 increased the vulnerability to rotenone-induced toxicity. (C) Treatment with DβHB and TUDCA fully protected both the non-tg strain and the DJ-1 knockdown nematodes; (+) p<0.01 compared to untreated nematodes of the same line. (*) p<0.01 as compared to non-tg of the same treatment group.