FIG. 6.
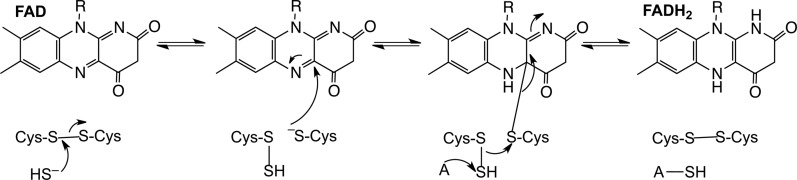
Minimal mechanism for the reaction catalyzed by human SQR. An active site disulfide is attacked by the incoming sulfide nucleophile and gives a persulfide and a free active site cysteine. The latter attacks the bound flavin forming a 4a adduct. Nucleophilic displacement by an acceptor (A) results in the transfer of the sulfane sulfur atom, reformation of the active site disulfide, and a two-electron reduction of the flavin.
