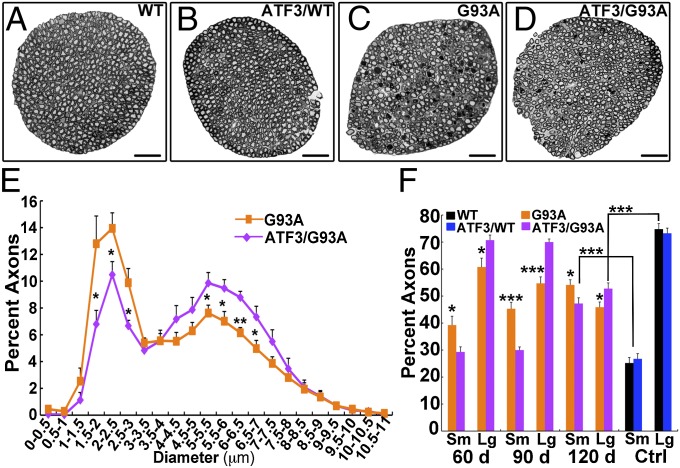
Fig. 2.
Axonal integrity is maintained in the ATF3/SOD1G93A mice. (A–D) Representative cross-section images of L5 ventral roots isolated from WT, ATF/WT, SOD1G93A, and ATF3/SOD1G93A mice at 90 d of age. (Scale bar: 50 μm.) (E and F) Quantification of axonal size per ventral root. Note that there is a reduction in the percentage of large-caliber axons and a concurrent increase in the percentage of small-caliber axons in the SOD1G93A mice compared with the ATF3/SOD1G93A mice (n = 6–9 mice per group per time point). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.001; ***P < 0.0001 by ANOVA with Bonferroni postanalysis. The total mean ± SEM values of axons counted per ventral root in SOD1G93A mice at 60, 90, and 120 d were 904 ± 24.56, 677.7 ± 23.08, and 586.54 ± 28.26, respectively. The total mean ± SEM values of axons counted per ventral root in ATF3/SOD1G93A mice at 60, 90, and 120 d were 781.83 ± 30.81, 803 ± 31.85, and 653.81 ± 9.27, respectively. In WT and ATF3/WT, the numbers of axons were 911.6 ± 14.99 and 980.5 ± 58.67, respectively. (E) Distribution of axonal diameter size in SOD1G93A compared with ATF3/SOD1G93A mice at 90 d of age is presented. (F) Percent of small-diameter axons (Sm; 0–3.5 μm) compared with large-diameter axons (Lg; 3.5–19 μm) per ventral root. Control (Ctrl) WT and ATF3/WT mice were 120 d of age.