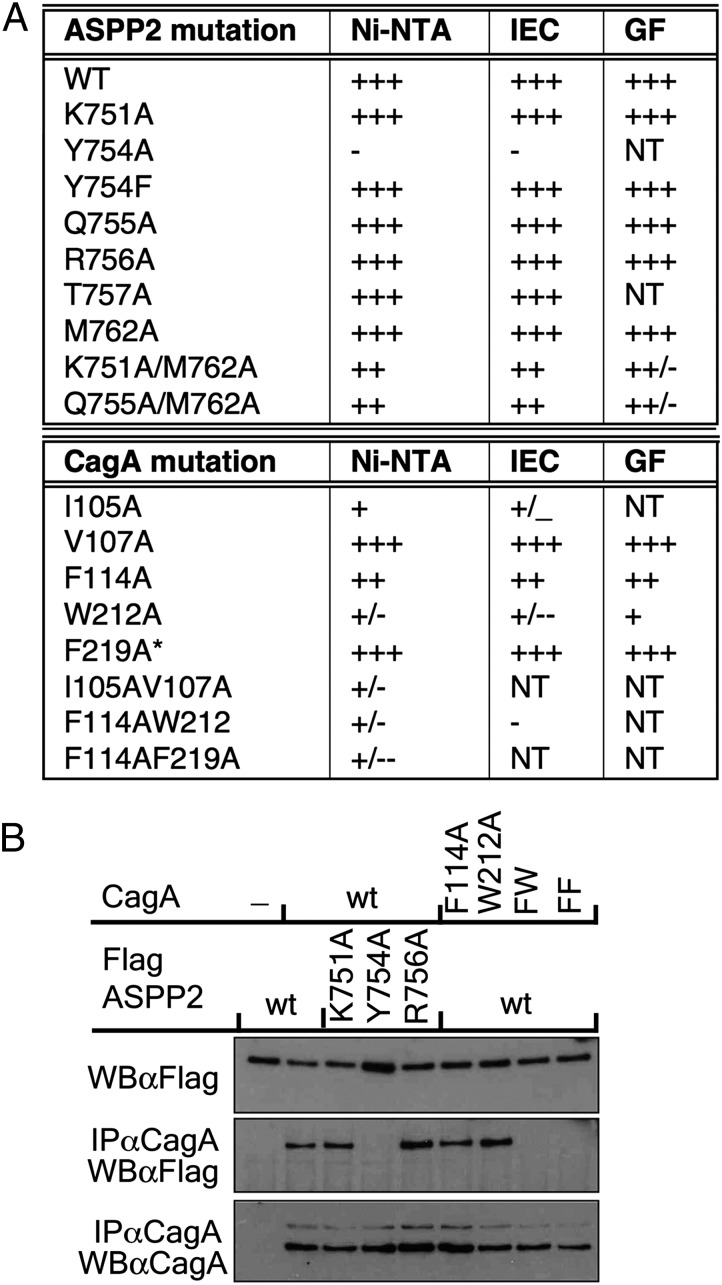
Fig. 3.
Structure-based mutagenesis of residues in the CagA–ASPP2 interface. (A) Summary of in vitro binding assays. GF, gel filtration, size exclusion chromatography of complexes; IEC, ion-exchange chromatography of complexes on SP Sepharose; Ni-NTA, affinity chromatography on Ni-NTA Sepharose of bacterial cell lysates coexpressing wild-type and mutant proteins as indicated; NT, not tested; *, additional mutation I35A/V37A (not involved in binding). (B) Contribution of different residues of ASPP2 and CagA to their interaction in cultured cells. HEK 293-T cells were cotransfected with wild-type or mutant CagA along with an expression construct of FLAG-tagged wild-type or mutant ASPP2, as indicated. Cells were lysed in Nonidet P-40 containing buffer, cellular extract was immunoprecipitated with anti-CagA antibody, and proteins were detected with indicated antibodies.