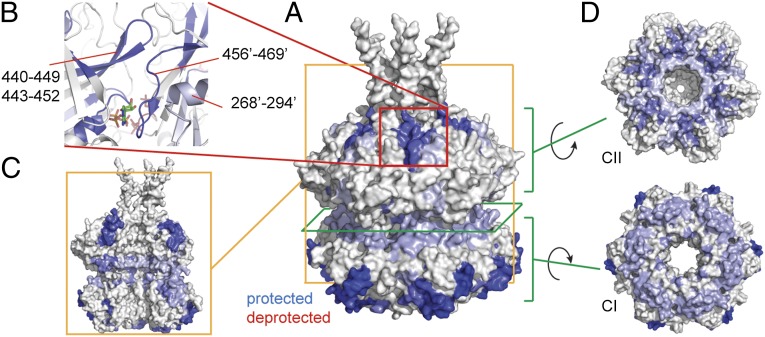
Fig. 4.
KaiB binding induces allosteric changes in KaiC. (A) Changes in deuterium uptake observed between free and bound KaiC. Only protected regions are detected. The changes in deuterium uptake are filtered to P < 0.01 and colored blue when protected in the KaiCB complex. Darker colored regions show stronger protection, and regions in white show no change or are not detected. The changes are plotted on a model of the KaiC hexamer of the crystal structure of KaiC (PDB ID code 3dvl); a hexamer of chain A was reconstructed as its entire C terminus is modeled in the PDB. (B) Zoom-in of the protected region on the CII domain. The indicated residues (a prime indicates residues from the adjacent chain) form one continuous binding surface that spans the interface between two subunits. The binding surface sits very close to the ATP-binding pocket. (C) Side view of three chains from the KaiC hexamer showing protection along the interface between KaiC subunits. (D) Views of the contact region between the CI and CII domains that becomes protected upon binding of KaiB.